Portfolio Architecture Examples: Automation Collection
This article is a continuation of a series of posts about our project named Portfolio Architectures. The previous post, Portfolio Architecture Examples: Healthcare Collection, begins with a project overview, introduction, and examples of tooling and workshops available for the project. You may want to refer back to that post to gain insight into the background of Portfolio Architectures before reading further.
Automation Collection
The collection featured today is centered around automation architectures. There are currently six architectures in this collection and we'll provide a short overview of each, leaving the in-depth exploration as an exercise for the reader.
Cloud Adoption
As enterprises adapt to public and/or private clouds, it is important to provide automation to manage and scale server deployments and to provide the capability to transition servers between data centers and cloud providers. This provides flexibility and portability for cloud adoption.
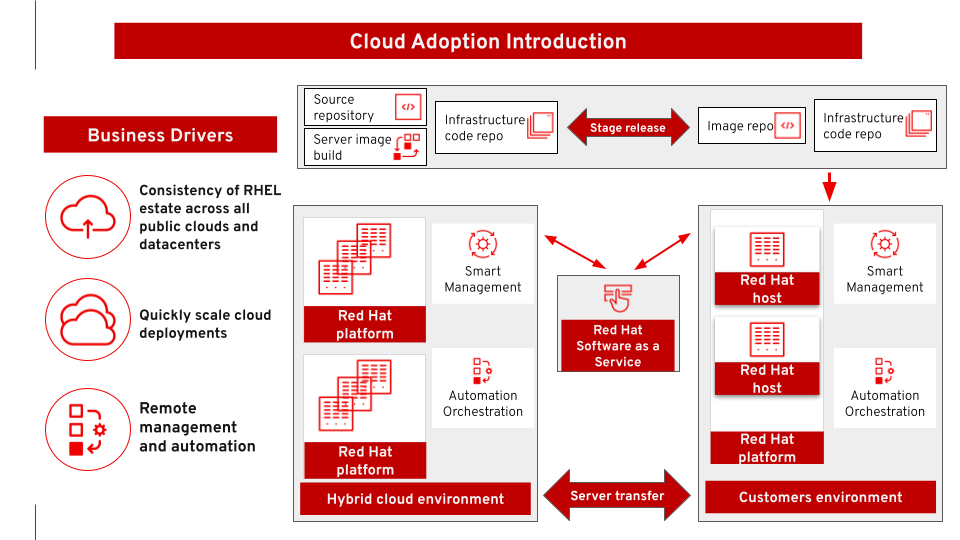
The use case is accelerating cloud adoption with effective automation for deploying and managing workloads across multiple cloud infrastructures according to performance, security, compliance, and cost requirements.
Cloud Factory
Instead of buying a cloud, large enterprises want a cloud factory, being able to deploy and manage the cloud in a modern and automated manner. This architecture covers deploying in an automated manner multiple instances of an OpenStack and Ceph-based cloud, following the principles of Infrastructure as Code.
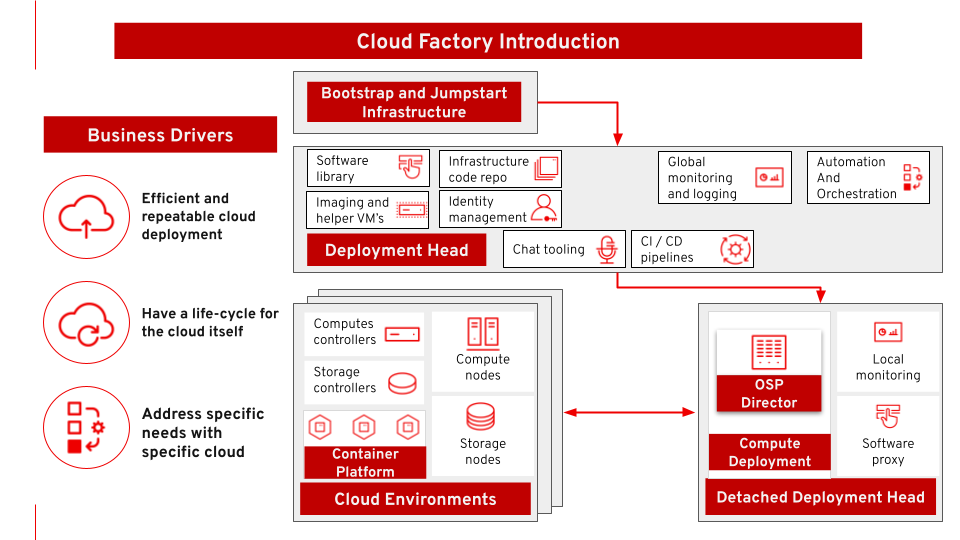
The use case is deploying multiple private clouds based on the same (infrastructure as) code using different parametrization.
Near Zero Downtime Maintenance for SAP
This architecture covers Near Zero Downtime Maintenance for RHEL servers hosting SAP workloads. SAP workloads are critical in the company and the maintenance windows are very strict, sometimes making it difficult for the system administrators to finish the update tasks properly in time. This solution allows for the application of OS patches, fixes, updates, DB patches, and new versions as well as SAP kernel updates, all while users can continue to work inside SAP without perceiving any disruption.
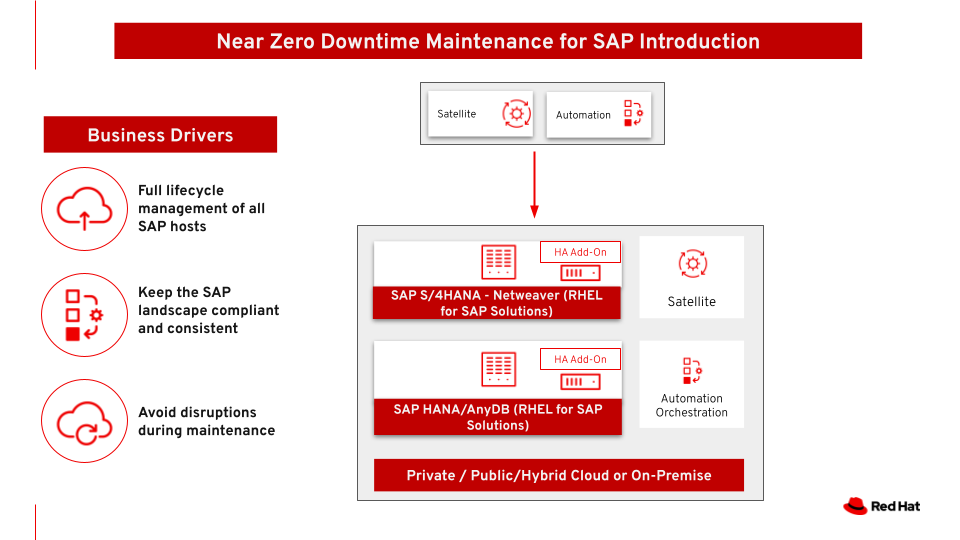
The use case is minimizing the downtime of the maintenance on SAP hosts so that users and processes can continue to work without perceiving any interruption.
Remote Server Management
This architecture covers remote server management. As more and more enterprises are deployed across different data centers and public and/or private clouds, it is important to provide consistency and security in an automated way across all of the servers in order to reduce risk and costs.
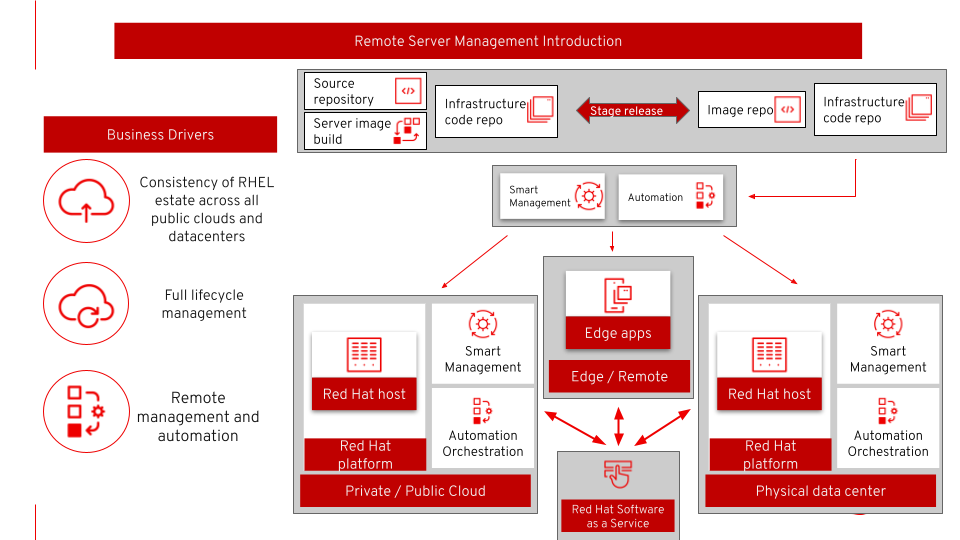
The use case is providing remote management for a consistent server estate across hybrid cloud and data centers with remote management, security, and data protection for a full lifecycle.
Self-Healing Infrastructure
Modern application infrastructure has, in many ways, gotten more complex as it has become more powerful and easy to consume. Keeping that infrastructure safe and compliant is a challenge for many organizations. One of the most powerful approaches to infrastructure management today is the combination of using historical data-driven insights and automation tools for applying remediation across a scaling estate of hosts in a targeted and prioritized manner.
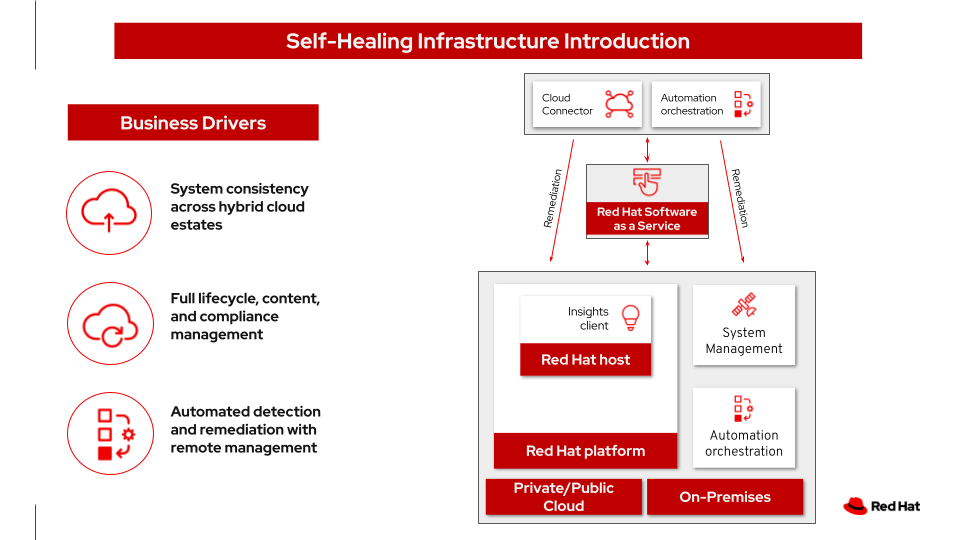
The use case is managing security, policy, and patches for a large number of servers in data centers or public/private clouds.
Smart Management for SAP
This architecture covers Smart Management for RHEL servers hosting SAP workloads. SAP landscapes are usually very complex with a high number of servers and lots of dependencies. Besides, SAP workloads are really performance-demanding and new recommendations need to be applied whenever a new release of the OS or the workload is certified. Maintaining that all the servers in these landscapes are aligned and up to date with the latest recommendations can be really challenging. On the other hand, being such critical systems, the need to prevent potential issues is of the utmost importance. The combination of Red Hat Insights with all its SAP specific rules to detect potential problems, Red Hat Automation Platform to remediate them before they occur, and Red Hat Satellite to manage the servers' lifecycle is a very powerful and robust tool to make sure that the SAP workloads will be healthy and operate smooth and performantly.
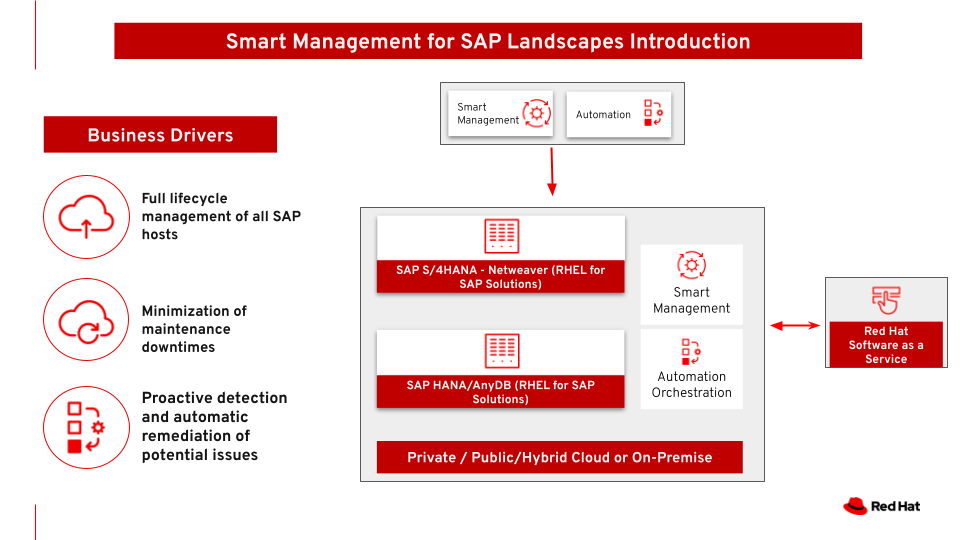
The use case is managing security, policy, and patches for all the servers in the SAP ecosystem (on-premise, public, private and hybrid cloud), making sure they are compliant with SAP and Red Hat’s recommendations through their entire lifecycle.
Additional Portfolio Architecture Solutions
If you are interested in more architecture solutions like these, feel free to export the Portfolio Architecture Examples repository. More architecture collections include:
- Application development
- Data engineering
- Edge
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Infrastructure
- Retail
- Telco

