Fun With SQL Using Postgres and Azure Data Studio
I have already written a few posts about PostgreSQL and this time I would like to take a step back and discuss some of the basics and at the same time share with you my experience of using Azure Data Studio.
Azure Data Studio is a cross-platform database tool for data professionals using the Microsoft family of on-premises and cloud data platforms on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It is very easy to install and offers a modern editor experience with IntelliSense, code snippets, source control integration, and an integrated terminal. It’s engineered with the data platform user in mind, with the built-in charting of query result sets and customizable dashboards. You can learn more about it from the official website on this link.
ADS also has notebooks that are similar to Jupiter notebooks for python and other languages and are great for combining formatted text with code. You can execute queries via a query window or via a notebook window. I will be using both of those. If you haven’t used ADS before, give it a try and you will like it.
Setup
I have installed the PostgreSQL database on my machine and I also have installed Azure Data Studio which I will use to execute various queries for the database. You can also use pgAdmin or any other tool as u wish. The following screenshot shows that I am connected to Postgres server.
Create a Database
Ok, let's start something simple and create a database. I use the notebook window from the Azure Data Studio (ADS) and execute the following SQL which created the database as intended.
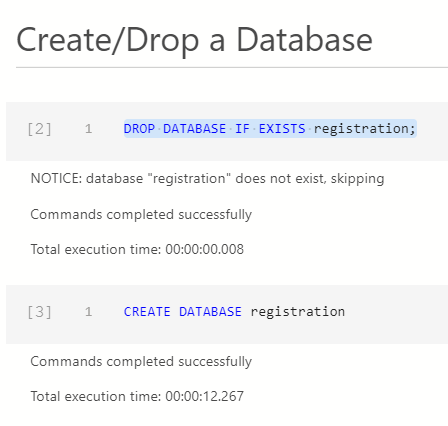
and here is the database:
Basic SQL Queries (Create, Alter, Select and Drop Basics)
In this section, we will refresh some basic SQL knowledge and some queries and their purposes.
Creating a Table
in DDL (Data Definition Language) SQL is very simple in PostgreSQL. Here is how the typical SQL looks like.
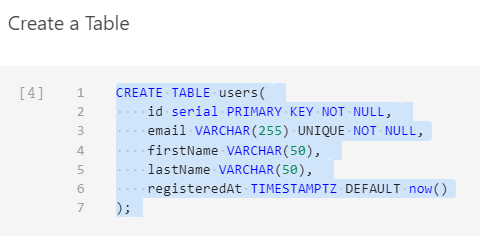
the keyword serial is PostgreSQL specific and it set up an auto-incrementing value and that is the typical way for the primary-key.
Deleting a Table
This is also very straight forward: Try not to do that in your production database :)
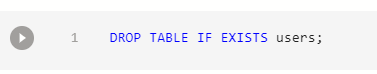
The if exists set up guards against error if the table doesn’t exist.
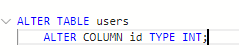
Altering a Table
is also very simple. e.g. if we want to alter a column in our table, the following is the syntax.
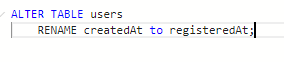
Another example showing renaming a column:
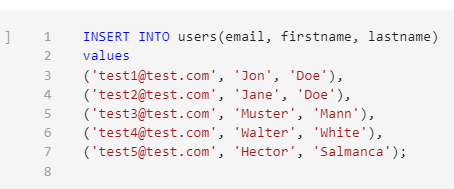
Insert Data
Let's insert and select some data using SQL.
Select Data From a Table
The following query shows the result and we can see that registeredat column has a default value as well.
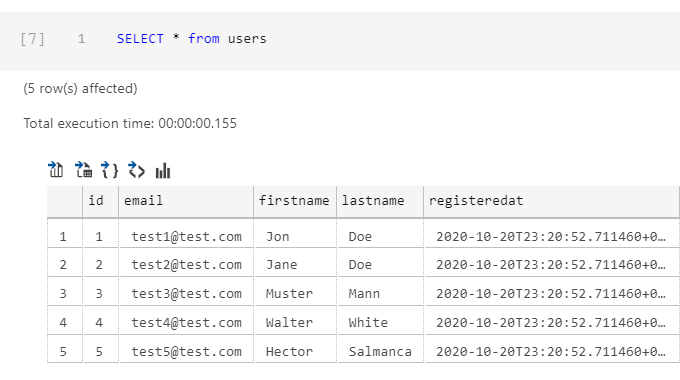
Select, Limit, and Page Results
To limit the result, Postgres uses limit as shown below (SQL-server uses TOP keyword):
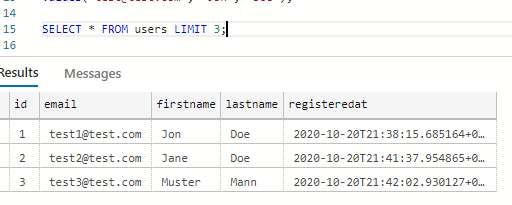
The other keyword which is very helpful and normally goes with limit is the keyword offset and used for pagination purposes:
the above query tells Postgres to grab the 3 users but skip the first 2 essentially making it a paging query.
Creating a Simple Function
Postgres has a lot of functions which we can use. We used now() function earlier which returns the current time. Another built-in function is random() which returns some random value as shown below:
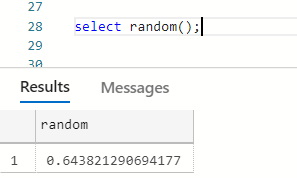
There are many functions available out of the box and we can create custom functions as well. Let's create a simple custom function using SQL.
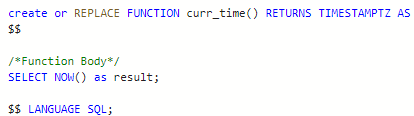
executing this SQL will result in function creation and we can use this function as per our needs.
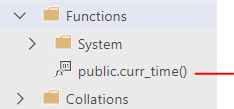
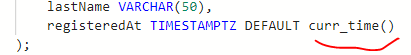
and here is how we can use it e.g. as a default value for a table column:
Summary
So, this was a very basic introduction to SQL, Postgres, and Azure Data Studio. Let me know if something is not clear. Till next time, happy coding.
References
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/azure-data-studio/quickstart-postgres?view=sql-server-ver15
- https://hexquote.com/net-core-postgresql-and-document-database/

