Configuring Git on Oracle Data Science Cloud Service
Hello to everyone!
In this article, we will establish a connection between Oracle Data Science Cloud Service and our remote Git repository. We will then send the code to our remote repository via the Data Science Cloud service. I hope it will be a useful article in terms of awareness.
Many Python libraries are available in Oracle's Data Science Cloud service. We can easily install libraries that are not installed from the terminal interface. Git is one example of software already installed in Oracle Data Science Cloud Service. You can open the terminal screen and check this setup with the command below.
xxxxxxxxxx
conda list
xxxxxxxxxx
cd block_storage
mkdir GitRepo
cd GitRepo
git init
git config --global user.email "emrahmete@gmail.com"
git config --global user.name "emrahmete"
git clone https://github.com/emrahmete/codebase
Yes, we have cloned our remote Git repository. When we look inside the GitRepo directory we created in the /blockstorage directory, we will see that our entire repository has been copied.
xxxxxxxxxx
cd /home/datascience/block_storage/GitRepo
ls -al
We saw that our codebase folder is coming. In this folder, we can access the code whenever we want, open and change it, and send it to our remote repository. Now, let's create a new file in the GitRepo directory, where I created a copy of our repository, and send it to our remote repository.
I will put my new file under the /home/datascience/block_storage/GitRepo/codebase/oracle/oml directory in my repository. Then, I will send it to the remote server from here. So let's start doing our operations.
xxxxxxxxxx
cd /home/datascience/block_storage/GitRepo/codebase/oracle/oml
echo 'Cloud Repo Test' > cloudtest.dat
ls -al more cloudtest.dat
git add .
git commit -m "DS Cloud Service Commit Test"
First of all, we wrote a simple text and created our cloudtest.dat file and committed this file to our local Git repository. Now, we have to push our remote Git repository. To do this, we will need to authorize a remote Git repository using our credentials on the screen. When the information is verified, our code will be sent to the remote server.
xxxxxxxxxx
git push
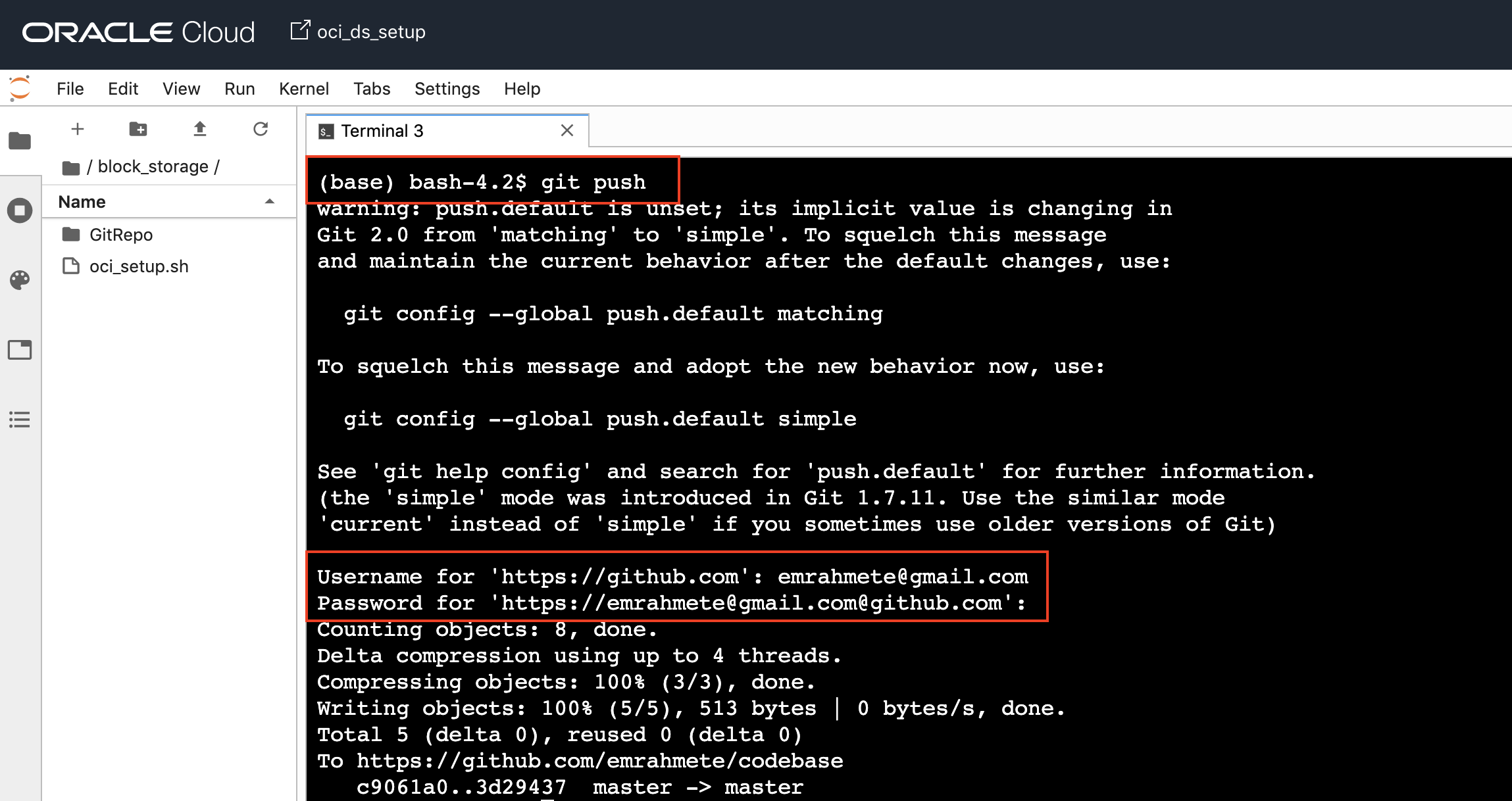
Yes, we have committed the newly created file in our local to the remote repo. Now, we can check if the file is going from the GitHub interface.
As we have seen, we have been able to send code very easily to our remote Git repository via Oracle Data Science Cloud Service.

