Real-Time Data Streaming on Cloud Platforms: Leveraging Cloud Features for Real-Time Insights
Editor's Note: The following is an article written for and published in DZone's 2024 Trend Report, Data Engineering: Enriching Data Pipelines, Expanding AI, and Expediting Analytics.
Businesses today rely significantly on data to drive customer engagement, make well-informed decisions, and optimize operations in the fast-paced digital world. For this reason, real-time data and analytics are becoming increasingly more necessary as the volume of data continues to grow. Real-time data enables businesses to respond instantly to changing market conditions, providing a competitive edge in various industries. Because of their robust infrastructure, scalability, and flexibility, cloud data platforms have become the best option for managing and analyzing real-time data streams.
This article explores the key aspects of real-time data streaming and analytics on cloud platforms, including architectures, integration strategies, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Cloud Data Platforms and Real-Time Data Streaming
Cloud data platforms and real-time data streaming have changed the way organizations manage and process data. Real-time streaming processes data as it is generated from different sources, unlike batch processing, where data is stored and processed at scheduled intervals. Cloud data platforms provide the necessary scalable infrastructure and services to ingest, store, and process these real-time data streams.
Some of the key features that make cloud platforms efficient in handling the complexities of real-time data streaming include:
- Scalability. Cloud platforms can automatically scale resources to handle fluctuating data volumes. This allows applications to perform consistently, even at peak loads.
- Low latency. Real-time analytics systems are designed to minimize latency, providing near-real-time insights and enabling businesses to react quickly to new data.
- Fault tolerance. Cloud platforms provide fault-tolerant systems to ensure continuous data processing without any disturbance, whether caused by hardware malfunctioning or network errors.
- Integration. These platforms are integrated with cloud services for storage, AI/ML tooling, and various data sources to create comprehensive data ecosystems.
- Security. Advanced security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications, ensure that real-time data remains secure and meets regulatory requirements.
- Monitoring and management tools. Cloud-based platforms offer dashboards, notifications, and additional monitoring instruments that enable enterprises to observe data flow and processing efficiency in real time.
This table highlights key tools from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, focusing on their primary features and the importance of each in real-time data processing and cloud infrastructure management:
Table 1
| Cloud service | key features | importance |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Auto Scaling |
|
|
| Amazon CloudWatch |
|
|
| Google Pub/Sub |
|
|
| Azure Data Factory |
|
|
| Azure Key Vault |
|
|
Cloud providers offer various features for real-time data streaming. When selecting a platform, consider factors like scalability, availability, and compatibility with data processing tools. Select a platform that fits your organization’s setup, security requirements, and data transfer needs.
To support your cloud platform and real-time data streaming, here are some key open-source technologies and frameworks:
- Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications.
- Apache Flink is a stream processing framework that supports complex event processing and stateful computations.
- Apache Spark Streaming is an extension of Apache Spark for handling real-time data.
- Kafka Connect is a framework that helps connect Kafka with different data sources and storage options. Connectors can be set up to transfer data between Kafka and outside systems.
Real-Time Data Architectures on Cloud Data Platforms
The implementation of real-time data analytics requires choosing the proper architecture that fits the special needs of an organization.
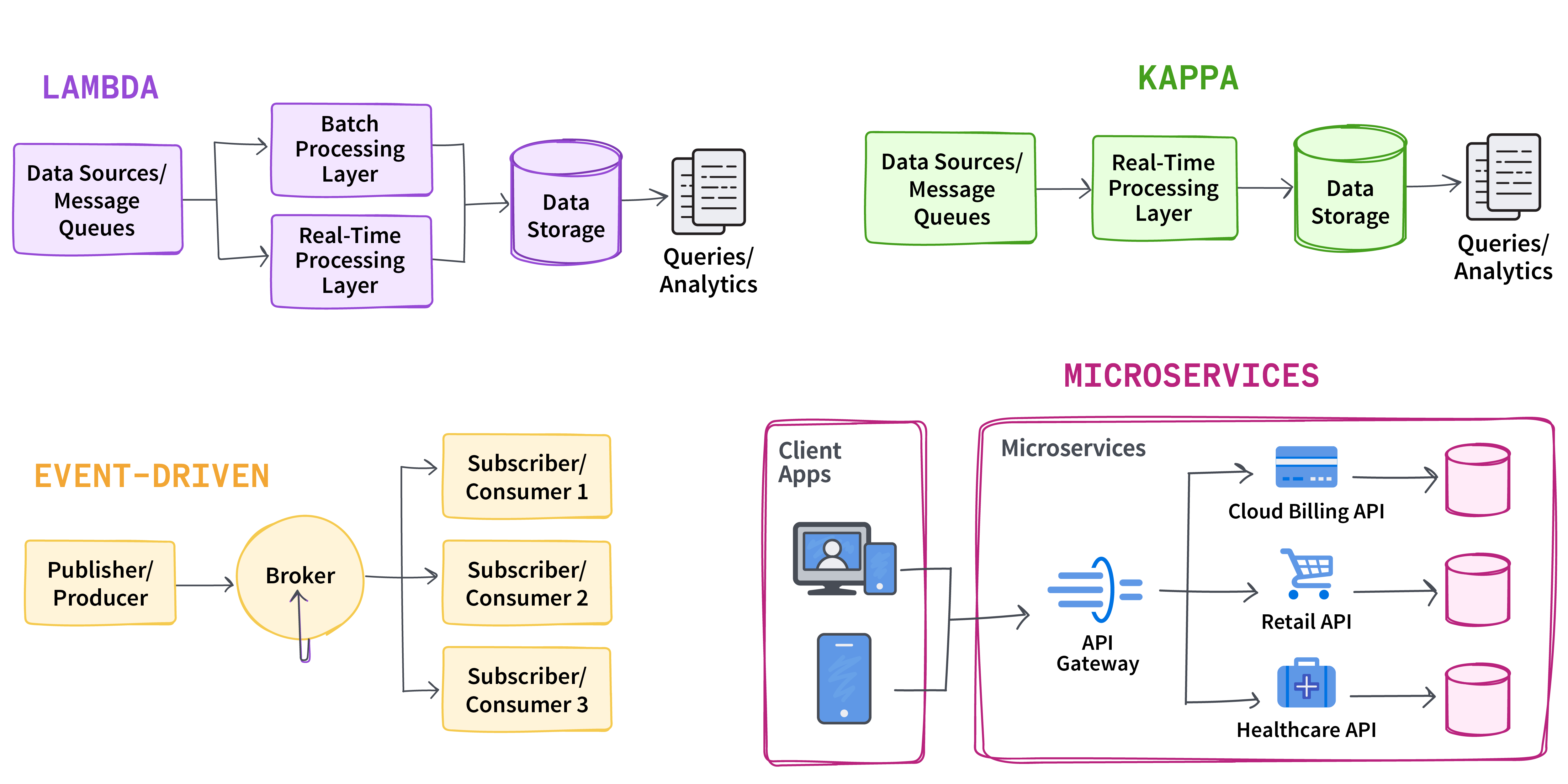
Common Architectures
Different data architectures offer various ways to manage real-time data. Here’s a comparison of the most popular real-time data architectures:
Table 2. Data architecture patterns and use cases
| architecture | description | ideal use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Lambda | Hybrid approach that combines batch and real-time processing; uses a batch layer to process historical data and a real-time layer for real-time data, merging the results for comprehensive analytics | Applications that need historical and real-time data |
| Kappa | Simplifies the Lambda architecture, focuses purely on real-time data processing, and removes the need for batch processing | Instances where only real-time data is required |
| Event driven | Processes data based on events triggered by specific actions or conditions, enabling real-time response to changes in data | Situations when instant notifications on data changes are needed |
| Microservices | Modular approach wherein the individual microservices handle specific tasks within the real-time data pipeline, lending scalability and flexibility | Complex systems that need to be modular and scalable |
These architectures offer adaptable solutions for different real-time data issues, whether the requirement is combining past data, concentrating on current data streams, responding to certain events, or handling complicated systems with modular services.
Figure 1. Common data architectures for real-time streaming
Integration of Real-Time Data in Cloud Platforms
Integrating real-time data with cloud platforms is changing how companies handle and understand their data. It offers quick insights and enhances decision making by using up-to-date information. For the integration process to be successful, you must select the right infrastructure, protocols, and data processing tools for your use case.
Key integration strategies include:
- Integration with on-premises systems. Many organizations combine cloud platforms with on-premises systems to operate in hybrid environments. To ensure data consistency and availability, it is necessary to have efficient real-time data transfer and synchronization between these systems.
- Integration with third-party APIs and software. The integration of real-time analytics solutions with third-party APIs — such as social media streams, financial data providers, or customer relationship management systems — can improve the quality of insights generated.
- Data transformation and enrichment. Before analysis, real-time data often needs to be transformed and enriched. Cloud platforms offer tools to make sure the data is in the right format and context for analysis.
- Ingestion and processing pipelines. Set up automated pipelines that manage data flow from the source to the target, improving real-time data handling without latency. These pipelines can be adjusted and tracked on the cloud platform, providing flexibility and control.
Integration of real-time data in cloud platforms involves data ingestion from different data sources and processing in real time by using stream processing frameworks like Apache Flink or Spark Streaming. Data integration can also be used on cloud platforms that support scalable and reliable stream processing. Finally, results are archived in cloud-based data lakes or warehouses, enabling users to visualize and analyze streaming data in real time.
Figure 2. Integration of real-time data streams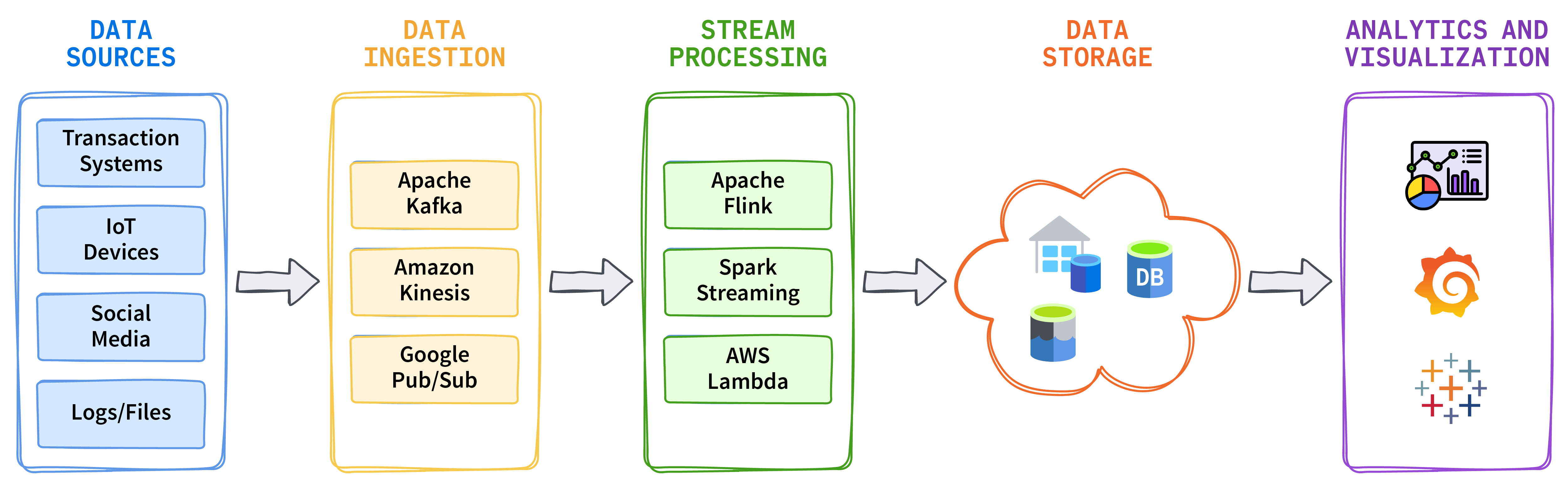
Here are the steps to set up real-time data pipelines on cloud platforms:
- Select the cloud platform that fits your organization's needs best.
- Determine the best data ingestion tool for your goals and requirements. One of the most popular data ingestion tools is Apache Kafkadue to its scalability and fault tolerance. If you’re planning to use a managed Kafka service, setup might be minimal. For self-managed Kafka, follow these steps:
- Identify the data sources to connect, like IoT devices, web logs, app events, social media feeds, or external APIs.
- Create virtual machines or instances on your cloud provider to host Kafka brokers. Install Kafka and adjust the configuration files as per your requirement.
- Create Kafka topics for different data streams and set up the partitions to distribute the topics across Kafka brokers. Here is the sample command to create topics using command line interface (CLI). The below command creates a topic
stream_datawith2partitions and a replication factor of2:
bash
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic stream_data --bootstrap-server your-broker:9092 --partitions 2 --replication-factor 2-
Configure Kafka producers to push real-time data to Kafka topics from various data sources:
- Utilize the Kafka Producer API to develop producer logic.
- Adjust batch settings for better performance (e.g.,
linger.ms,batch.size). - Set a retry policy to manage temporary failures.
Sample Kafka Producer configuration properties
bootstrap.servers=your-kafka-broker:9092
key.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
batch.size=15350
linger.ms=5
retries=2
acks=allbatch.size sets the max size (bytes) of batch records, linger.ms controls the wait time, and the acks=all setting ensures that data is confirmed only after it has been replicated.
-
Consume messages from Kafka topics by setting up Kafka consumers that subscribed to a topic and process the streaming messages.
-
Once data is added to Kafka, you can use stream processing tools like Apache Flink, Apache Spark, or Kafka Streams to transform, aggregate, and enrich data in real time. These tools operate simultaneously and send the results to other systems.
-
For data storage and retention, create a real-time data pipeline connecting your stream processing engine to analytics services like BigQuery, Redshift, or other cloud storage services.
-
After you collect and save data, use tools such as Grafana, Tableau, or Power BI for analytics and visualization in near real time to enable data-driven decision making.
-
Effective monitoring, scaling, and security are essential for a reliable real-time data pipeline.
- Use Kafka's metrics and monitoring tools or Prometheus with Grafana for visual displays.
- Set up autoscaling for Kafka or message brokers to handle sudden increases in load.
- Leverage Kafka's built-in features or integrate with cloud services to manage access.
- Enable TLS for data encryption in transit and use encrypted storage for data at rest.
Combining Cloud Data Platforms With Real-Time Data Streaming: Benefits and Challenges
The real-time data and analytics provided by cloud platforms provide several advantages, including:
- Improved decision making. Having instant access to data provides real-time insights, helping organizations to make proactive and informed decisions that can affect their business outcomes.
- Improved customer experience. Through personalized interactions, organizations can engage with customers in real time to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational efficiency. Automation and real-time monitoring help find and fix issues faster, reducing manual work and streamlining operations.
- Flexibility and scalability. Cloud platforms allow organizations to adjust their resources according to demand, so they only pay for the services they use while keeping their operations running smoothly.
- Cost effectiveness. Pay-as-you-go models help organizations use their resources more efficiently by lowering spending on infrastructure and hardware.
Despite the advantages, there are many challenges in implementing real-time data and analytics on cloud platforms, including:
- Data latency and consistency. Applications need to find a balance between how fast they process data and how accurate and consistent that data is, which can be challenging in complex settings.
- Scalability concerns. Even though cloud platforms offer scalability, handling large-scale real-time processing in practice can be quite challenging in terms of planning and optimization.
- Integration complexity. Integration of real-time data streaming presses with legacy systems, on-prem infrastructure, or previously implemented solutions can be difficult, especially in hybrid environments; it may need a lot of customization.
- Data security and privacy. Data security must be maintained throughout the entire process, from collection to storage and analysis. It is important to ensure that real-time data complies with regulations like GDPR and to keep security strong across different systems.
- Cost management. Cloud platforms are cost effective; however, managing costs can become challenging when processing large volumes of data in real time. It’s important to regularly monitor and manage expenses.
Future Trends in Real-Time Data and Analytics in Cloud Platforms
The future of real-time data and analytics in cloud platforms is promising, with several trends set to shape the landscape. A few of these trends are outlined below:
- Innovations in AI and machine learning will have a significant impact on cloud data platforms and real-time data streaming. By integrating AI/ML models into data pipelines, decision-making processes can be automated, predictive insights can be obtained, and data-driven applications can be improved.
- More real-time data processing is needed closer to the source of data generation as a result of the growth of edge computing and IoT devices. In order to lower latency and minimize bandwidth usage, edge computing allows data to be processed on devices located at the network's edge.
- Serverless computing is streamlining the deployment and management of real-time data pipelines, reducing the operational burden on businesses. Because of its scalability and affordability, serverless computing models — where the cloud provider manages the infrastructure — are becoming increasingly more common for processing data in real time.
In order to support the growing complexity of real-time data environments, these emerging technology trends will offer more flexible and decentralized approaches to data management.
Conclusion
Real-time data and analytics are changing how systems are built, and cloud data platforms offer the scalability tools and infrastructure needed to efficiently manage real-time data streams. Businesses that use real-time data and analytics on their cloud platforms will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world as technology continues to advance. Emerging trends like serverless architectures, AI integration, and edge computing will further enhance the value of real-time data analytics. These improvements will lead to new ideas in data processing and system performance, influencing the future of real-time data management.
This is an excerpt from DZone's 2024 Trend Report,
Data Engineering: Enriching Data Pipelines, Expanding AI, and Expediting Analytics.
Read the Free Report

