Spring Cloud and Spring Boot, Part 4: Implementing Spring Boot Admin Server
In this article, you will going to learn Spring Admin Server and you can also read below 3 articles describing other spring cloud and spring boot capabilities like implementing Eureka Server, Zipkin Server and Spring Cloud Config Server.
Implementing Eureka Server
Implementing Zipkin Server
Implementing Spring Cloud Config Server
What is Spring Boot Admin Server?
It is difficult to monitor the microservices using Spring Boot Actuator Endpoint. If the number of microservices increases, it means the number of actuator endpoints also increases. In such scenarios, it is difficult to manage and monitoring the microservices.
Spring Boot Admin Server manage and monitor your all microservices. To handle such situations, CodeCentric provides Spring Boot Admin UI which can manage and monitor all the microservices Spring Boot Actuator at single place.
To achieve this, you need to create Spring Boot Admin Server application and add below two dependencies in POM.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-server-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>Implementing Spring Boot Admin Server
Creating Spring Boot Admin Server
Navigate to https://start.spring.io/ and create a project template. Provide project metadata like Group, Artifact and add below dependencies/modules. Click Generate Project and it will download .zip Spring-based project and you can unzip the downloaded project and import in eclipse as maven project.
Spring Admin Server
Web
- Actuator
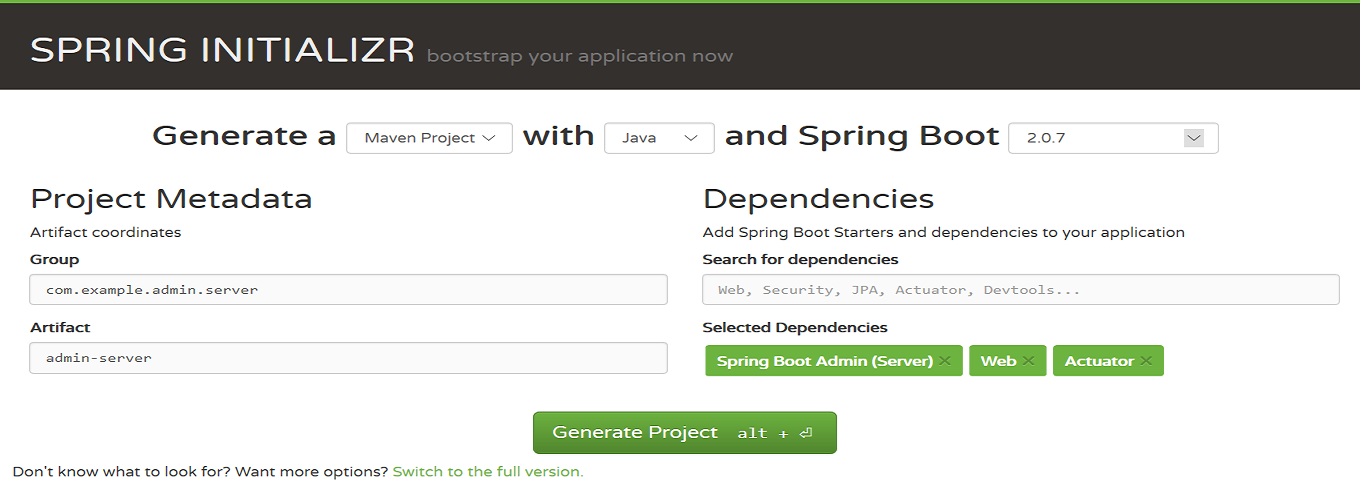
POM.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example.admin.server</groupId>
<artifactId>admin-server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>admin-server</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-boot-admin.version>2.0.4</spring-boot-admin.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-server-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot-admin.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Spring Boot Starter Application
Now you need to open AdminServerApplication.java and add the annotation @EnableAdminServer on the top of the class as shown below.
package com.example.admin.server.adminserver;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import de.codecentric.boot.admin.server.config.EnableAdminServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
public class AdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}Application Properties File
You need to add below list of properties in application.properties located at src/main/resources of your application.
spring.application.name=admin-server
server.port=9090Running Spring Boot Admin Server
Run the Spring Cloud Config Server as Java application and browse the URL http://localhost:9090/.
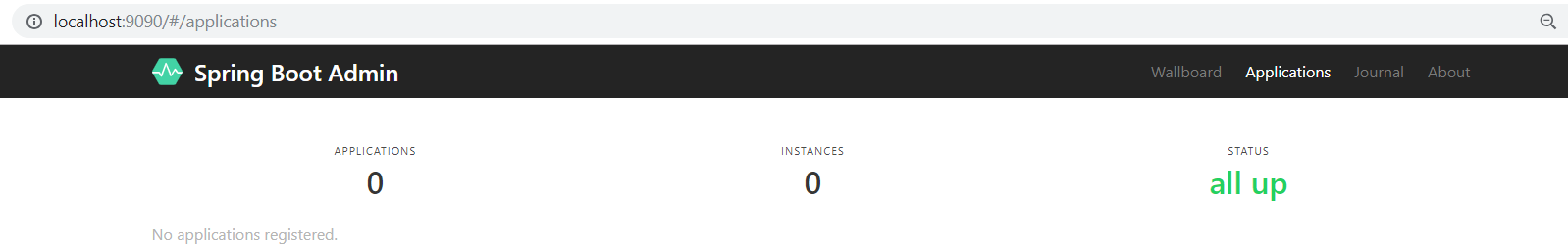
Currently, you cannot see anything on the dashboard. You need to register the client application with Spring Boot Admin Server.
Registering Client Application With Spring Boot Admin Server
Adding POM dependency
You need to add the below POM dependency in the POM.xml of the client application.
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>Application Properties File
You need to add below two properties file in application.properties file of the client application.
spring.boot.admin.client.url=http://localhost:9090
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*spring.boot.admin.client.url: determines the path of Spring Boot Admin Server.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include: determines which actuator endpoints needs to be exposed and * represents all actuator enpoints will be exposed.
Running Client Application
Before running the application, you need to make sure Spring Boot Admin Server is up and running. Run the client application as a Java application.
Navigate to http://localhost:9090 (Spring Boot Admin Server). Now, you will see your client application registered in Spring Boot Admin Server.
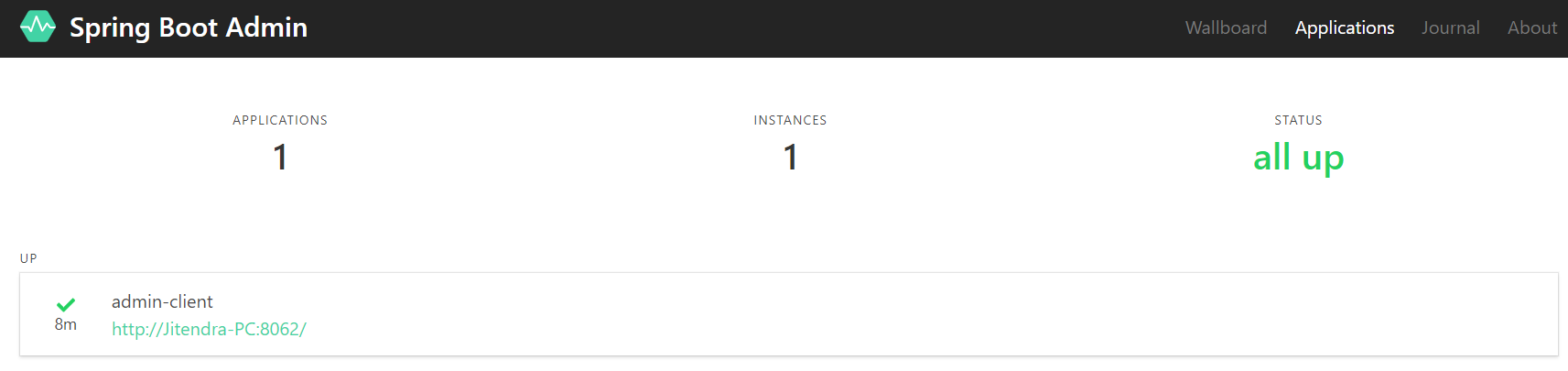
Viewing Monitoring Details on Spring Boot Admin Server
You can view more details like metrics, CPU usage, memory usage, etc., by clicking on the instance of your microservice shown in above image.
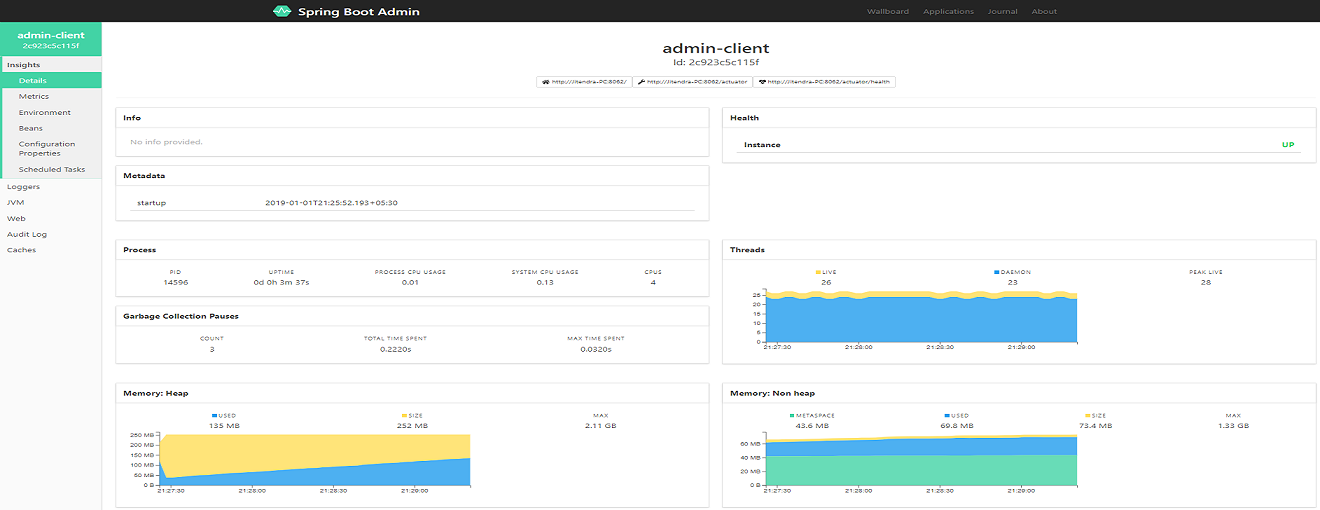
Now, you know how to implement Spring Boot Admin Server.

