Paginating JOINs via jOOQ and DENSE_RANK()
Working With DENSE_RANK()
DENSE_RANK() is a window function that assigns a rank to each row within a partition or result set with no gaps in ranking values. A simple example is shown here:
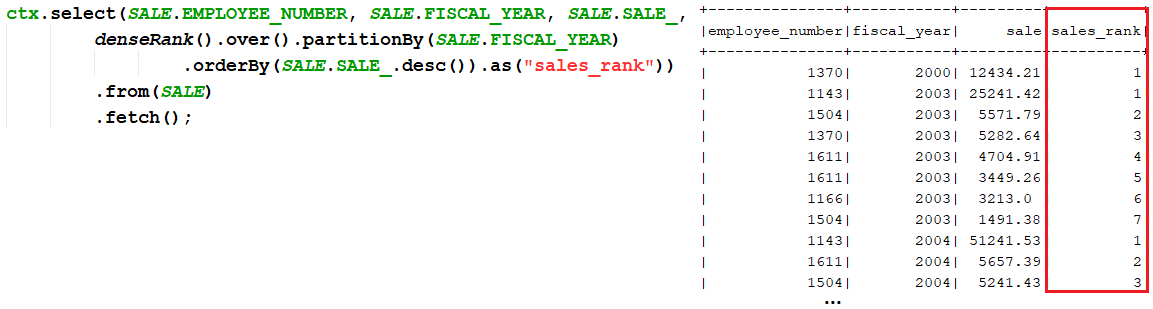
Let's assume that we want to rank employees (EMPLOYEE) in offices (OFFICE) by their salary (EMPLOYEE.SALARY). Expressing this via jOOQ and DENSE_RANK() can be done as follows:
ctx.select(EMPLOYEE.FIRST_NAME, EMPLOYEE.LAST_NAME, EMPLOYEE.SALARY,
OFFICE.CITY, OFFICE.COUNTRY,
OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE,
denseRank().over().partitionBy(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE)
.orderBy(EMPLOYEE.SALARY.desc()).as("salary_rank"))
.from(EMPLOYEE)
.innerJoin(OFFICE)
.on(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE.eq(EMPLOYEE.OFFICE_CODE))
.fetch();An output fragment looks like this (notice that the employees having the same salary get the same rank):
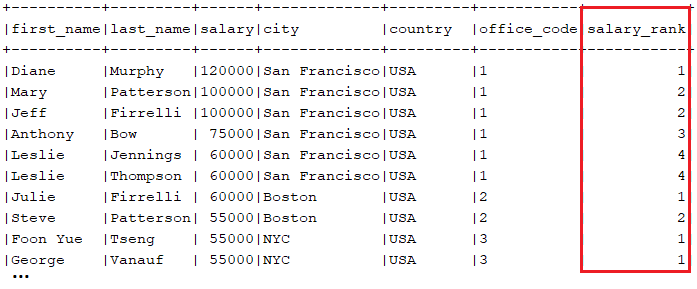
Next, let's use DENSE_RANK() for selecting the highest salary from each office, including duplicates. This time, let's use the QUALIFY clause as well. The code is illustrated in the following snippet:
select(EMPLOYEE.FIRST_NAME, EMPLOYEE.LAST_NAME,
EMPLOYEE.SALARY, OFFICE.CITY, OFFICE.COUNTRY,
OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE)
.from(EMPLOYEE)
.innerJoin(OFFICE)
.on(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE.eq(EMPLOYEE.OFFICE_CODE))
.qualify(denseRank().over().partitionBy(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE)
.orderBy(EMPLOYEE.SALARY.desc()).eq(1))
.fetch();Before going further, here is a nice read called "The Difference Between ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), and DENSE_RANK()." You can check out these examples in the DenseRank bundled code.
Paginating JOINs via DENSE_RANK()
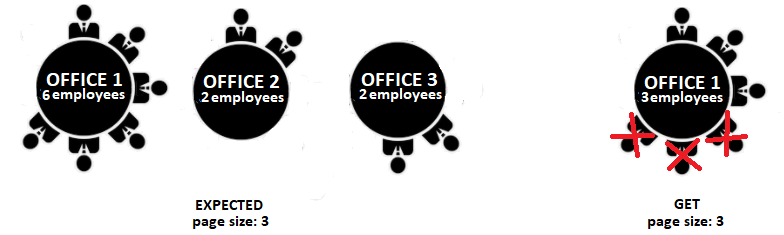
Let's assume that we want to paginate offices (OFFICE) with employees (EMPLOYEE). If we apply a classical offset or keyset pagination to the JOIN between OFFICE and EMPLOYEE, then the result is prone to be truncated. Therefore, an office can be fetched with only a subset of its employees. For instance, while we think of a result page of size 3 as containing three offices with all their employees, we instead get a single office with three employees (even if this office has more employees). The following figure reveals what we expect versus what we get from a page of size 3 (offices):
In order to obtain a result set like the one on the left-hand side of the preceding figure, we can rely on the DENSE_RANK() window function, which assigns a sequential number to different values of a within each group b, as shown in the following jOOQ query:
Map<Office, List<Employee>> result = ctx.select().from(
select(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE, OFFICE...,
EMPLOYEE.FIRST_NAME, EMPLOYEE...,
denseRank().over().orderBy(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE, OFFICE.CITY).as("rank"))
.from(OFFICE)
.join(EMPLOYEE)
.on(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE.eq(EMPLOYEE.OFFICE_CODE)).asTable("t"))
.where(field(name("t", "rank")).between(start, end))
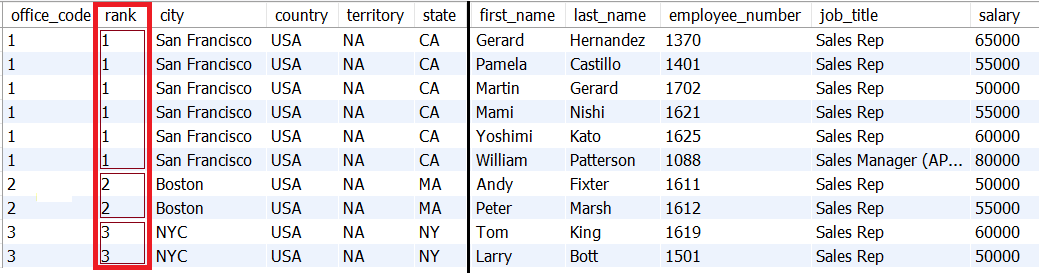
.fetchGroups(Office.class, Employee.class);The start and end variables represent the range of offices set via DENSE_RANK(). The following figure should clarify this aspect where start = 1 and end = 3 (the next page of the three offices is between start = 4 and end = 6):
Here is a more compact version of the previous query, using the QUALIFY clause:
Map<Office, List<Employee>> result =
ctx.select(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE, OFFICE...,
EMPLOYEE.FIRST_NAME, EMPLOYEE...)
.from(OFFICE)
.join(EMPLOYEE)
.on(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE.eq(EMPLOYEE.OFFICE_CODE))
.qualify(denseRank().over().orderBy(OFFICE.OFFICE_CODE, OFFICE.CITY)
.between(start, end))
.fetchGroups(Office.class, Employee.class);You can check out the complete example named DenseRankPagination for MySQL. The returned Map<Office, List<Employee>> is serialized to JSON via a classical Spring Boot controller.
There are chances that you are not familiar with the QUALIFY clause, so here is a brief overview.
The QUALIFY Clause
Some databases (for instance, Snowflake) support a clause named QUALIFY. Via this clause, we can filter (apply a predicate) the results of window functions. Mainly, a SELECT … QUALIFY clause is evaluated after window functions are computed, so after Window Functions (step 6) and before DISTINCT (Step 8):
The syntax of QUALIFY is QUALIFY <predicate>, and in the following screenshot, you can see how it makes the difference (this query returns every 10th product from the PRODUCT table via the ROW_NUMBER() window function):

By using the QUALIFY clause, we eliminate the subquery and the code is less verbose. Even if this clause has poor native support among database vendors, jOOQ emulates it for all the supported dialects. Cool, right?!
Explore further in my book, jOOQ Masterclass.

