Demystifying Cloud Trends: Statistics and Strategies for Robust Security
According to Gartner research, the Global Public Cloud Services spending is estimated to Total $679 Billion in 2024 from $491 Billion in 2022. The adoption is estimated to surpass $1 Trillion by 2027. An interesting aspect in O'Reilly's latest Cloud Adoption report based on a global survey conducted is that 90% of the responders are using the cloud to support their business. Diving further into the report, it is evident that 67% of the responders have adopted the public cloud, and 45% are using the private cloud. One of the key takeaways from the State of the Cloud report from Flexera that studied the organization’s cloud adoption progress around the world is that 92 % of the enterprise organizations (organizations with more than 1000 employees) are adopting a multi-cloud strategy, and 80% of the organizations are adopting hybrid cloud model.
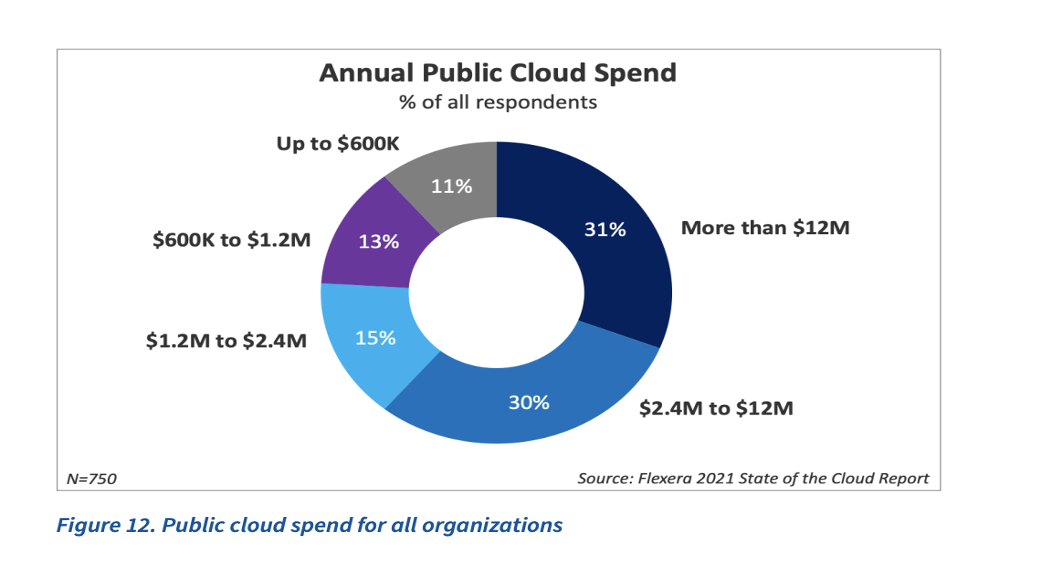
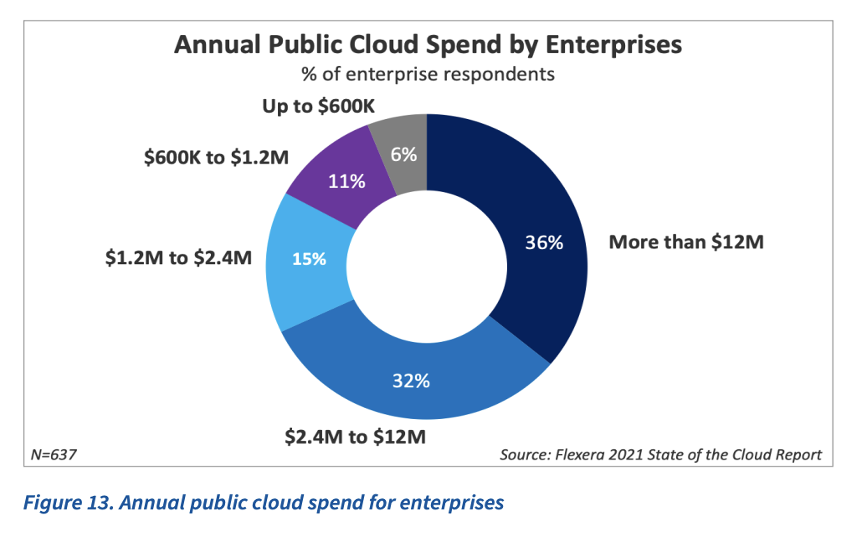
One of the major areas of cloud spending by organizations of all sizes is public cloud. 31% of the respondents reported spending at least $12 million annually, and 76% of the respondents spend around $1.2 million annually on public cloud. Diving further into the report findings, it's evident that 36% of the enterprises (organizations with more than 1000 employees) that have responded spend more than $12 million annually on public cloud.
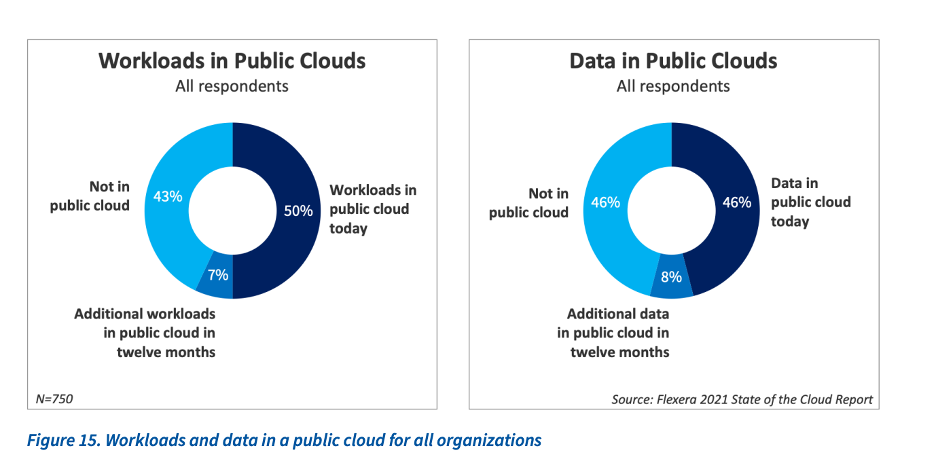
Based on the Flexera state of the cloud report, more than 50 % of the data and workloads are in the public cloud, and this adoption model is estimated to grow in the future. These evaluations and findings in these reports bring the aspect of cloud security to the forefront.
Cloud Security Challenges
As cloud adoption continues to grow, the concerns related to cloud security also increase. According to the research conducted by Ponemon Institute, the yearly financial average loss due to compromised cloud accounts study was estimated at 6.2 million dollars.
Here are a few key statistics related to cloud security:
- According to Radware's multi-cloud report, 69% of organizations have reported experiencing data breaches due to multi-cloud security configurations.
- Based on the Flexera State of the Cloud report, 82% of organizations reported that managing cloud costs is one of the biggest cloud security challenges, and 79% of the organizations consider cloud security as their primary challenge.
- As per IBM, the average total cost of a data breach is estimated to be $4.35M.
- According to the Verizon report, Human-related breaches such as social attacks, mistakes, and abuse contribute to 82% of the incidents.
- Interestingly, out of all businesses that are most affected by cloud security incidents, startups contribute to 89%.

Statistics that summarize the organization’s top cloud challenges.
Strategies for Robust Cloud Security
A robust and secure cloud environment at any point in time is a moving target. As the adoption landscape progresses and evolves, so does the effectiveness of the organization’s cloud security state, which has been continuously evaluated. To start with, here are a few key cloud security strategies that organizations could adopt to secure the adoption landscape.
Adopt a Comprehensive Security Framework
Adopting a comprehensive security framework is the fundamental aspect of the goal of establishing a robust security posture in the cloud environments. The key aspects of a security framework are that it provides a structured approach, best practices, and guidelines for identifying, implementing, and managing security controls.
Here are a few Cloud Security frameworks that organizations could adopt: MITRE ATT&CK, Center for Internet Security (CIS), Cloud Security Alliance’s Security Trust Assurance and Risk (CSA STAR), ISO/IEC 27017:2015 and a few cloud provider-developed frameworks such as AWS Foundation Security Best Practices Standard Microsoft cloud security benchmarks and IBM Cloud Security framework.
Shared Responsibility Model
The Shared Responsibility Model is a security and compliance framework that defines the responsibilities of cloud service providers (CSPs) and cloud customers for securing every aspect of the cloud environment, including hardware, infrastructure, endpoints, data, configurations, settings, operating system (OS), network controls and access rights. In basic terms, this model helps clarify who is responsible for securing various aspects of the cloud infrastructure, services, and data.
The division of responsibilities varies depending on the cloud deployment model (Infrastructure as a Service— IaaS, Platform as a Service — PaaS, or Software as a Service — SaaS).
Robust IAM and MFA
Implementing strong IAM practices enforcing the principle of least privilege to restrict access rights for users and systems and regularly reviewing and updating access permissions can have a major positive impact on an organization’s cloud security posture. It’s as simple as granting users and other cloud resources the authorization to access the required resources only to a required extent.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that only authorized users have access to resources and data. This additional layer is something that the user knows (such as passwords) and the user has (MFA token device). The MFA approach mainly helps in mitigating credential-based attacks and aids in dynamic adaptation to perceived risk factors such as logging in from a new device or location, etc.
Ensuring Data and Network Security
Data and network security are critical aspects of overall cloud security. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and securing the communication channels within the cloud environment is essential for a healthy and robust cloud security posture. Data security can be achieved by implementing rest encryption and transit encryption. Data classification, lifecycle management, and implementing appropriate access controls can help achieve the desired level of data security. Regular data backups and auditing can minimize data management risks in the cloud.
Network security plays a critical role equal to data security as network security deals with fortifying the communication channels in, out, and within the cloud landscape. Network security can be achieved by implementing efficient Firewalls, Network Segmentation, Intrusion detection and prevention systems, effective access controls, securing APIs/Containers, DDoS protection, etc.
Security Training and Competency Improvement
Cloud Security training and awareness initiatives are integral to building a strong security culture within an organization. These programs empower employees to contribute actively to the organization's security objectives and foster collective responsibility for maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Cloud misconfigurations contribute heavily to the data and security breaches that occur. One of the most common causes of cloud misconfiguration is misunderstanding who is responsible for securing cloud assets. Regular cloud competency improvement also helps in keeping updated with the latest advancements and security tools and practices.
Conclusion
“By 2028, it will shift from being a technology disruptor to becoming a necessary component for maintaining business competitiveness”, according to Gartner, Inc. It’s not a surprising prediction that an organization’s business outcome will be dependent on its Cloud strategy. Such a tremendous cloud adoption rate across industries also presents a greater risk of cloud security. As an outcome of a cloud breach, the cloud is expensive both financially and in terms of reputation, and the emphasis on Cloud Security is justified.

