How to Build Microservices in Python
microservices design helps alleviate some problems associated with the monolithic model. implementing microservices is perhaps one of the greatest ways to improve the productivity of a software engineering team. this is especially true if the following takes place:
- you deploy only the component that was changed (as opposed to the whole application). this keeps the deployments and the tests manageable.
- if multiple team members are working on the application, they need to wait until everyone is done with development and testing and ready to move forward . however, with the microservices services model, whenever each piece of functionality is ready, it could be deployed.
- each microservice runs in its own process space, so if we want to scale for any reason, we can scale the particular microservice that needs more resources instead of scaling the entire application .
- when one microservice needs to communicate with another micro-service, it uses a lightweight protocol such as http.
this post examines how to deploy microservices created using python and django on nginx and uwsgi.
before going into the details of a microservices design, let's understand and examine how a typical monolithic application looks.
monolithic design
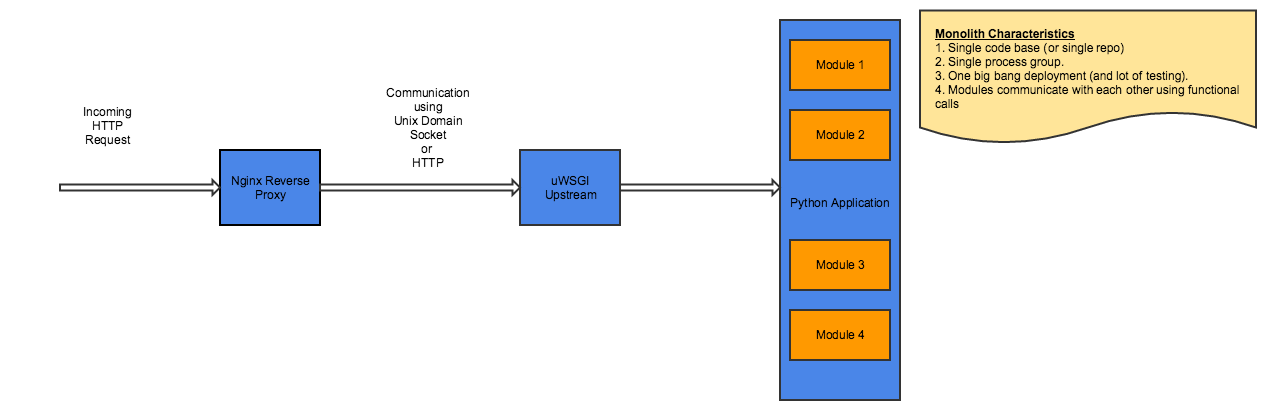
however, with breaking the functionality into logically isolated micro-services, this is how the design would like.
microservices design
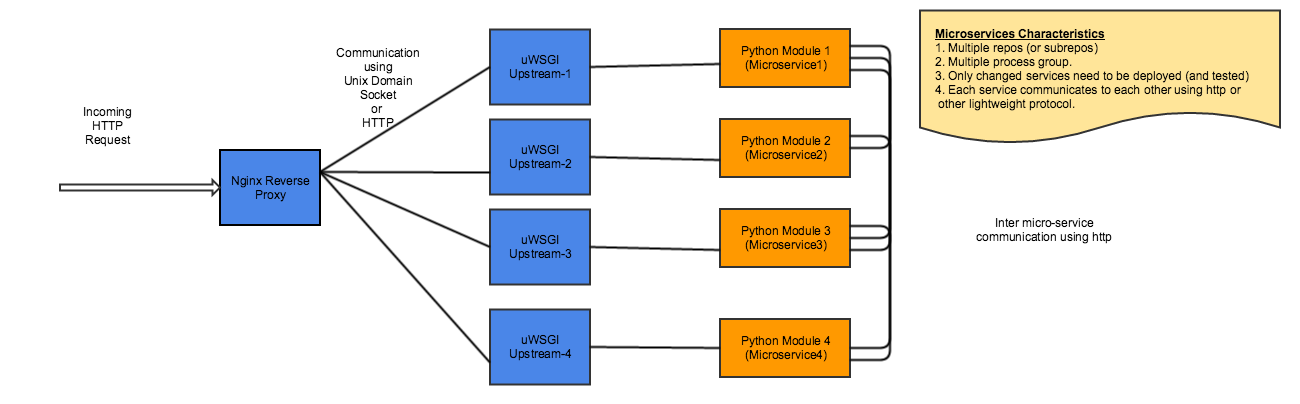
now, let's examine how the configuration would look for a python and django application that runs on nginx on a typical linux server.
because the application code is spread across multiple repos (or subrepos) grouped by logically independent code, this will be the typical organization of the application directories on the server.
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-34-107 www]$ pwd
/opt/www
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-34-107 www]$ ls -lrt
total 8
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 oct 12 14:09 microservice1
drwxr-xr-x. 7 root root 4096 oct 12 19:00 microservice2
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 oct 12 14:09 microservice3
drwxr-xr-x. 7 root root 4096 oct 12 19:00 microservice4nginx, which is typically deployed a front-end gateway or a reverse proxy, will have this configuration:
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-34-107 servicea]$ cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/service.conf
upstream django1 {
server unix:///opt/www/service1/uwsgi.sock; # for a file socket
}
upstream django2 {
server unix:///opt/www/service2/uwsgi.sock; # for a file socket
}
upstream django3 {
server unix:///opt/www/service3/uwsgi.sock; # for a file socket
}
upstream django4 {
server unix:///opt/www/service4/uwsgi.sock; # for a file socket
}
server {
# the port your site will be served on
listen 80;
# the domain name it will serve for
server_name localhost;
charset utf-8;
# max upload size
client_max_body_size 75m; # adjust to taste
location /api/service1/ {
uwsgi_pass django1;
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
}
location /api/service2/ {
uwsgi_pass django2;
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
}
location /api/service3/ {
uwsgi_pass django3;
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
}
location /api/service4/ {
uwsgi_pass django4;
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
}multiple uwsgi processes have to be created that would process the request for each microservice:
/usr/bin/uwsgi --socket=/opt/www/service1/uwsgi.sock --module=microservice-test.wsgi --master=true --chdir=/opt/www/service1
/usr/bin/uwsgi --socket=/opt/www/service2/uwsgi.sock --module=microservice-test.wsgi --master=true --chdir=/opt/www/service2
/usr/bin/uwsgi --socket=/opt/www/service3/uwsgi.sock --module=microservice-test.wsgi --master=true --chdir=/opt/www/service3
/usr/bin/uwsgi --socket=/opt/www/service4/uwsgi.sock --module=microservice-test.wsgi --master=true --chdir=/opt/www/service4

