Role of Artificial Intelligence for Government
Introduction
For the last 20 years, the research on artificial intelligence has been very aggressive, which has resulted in great innovations. Big data, robotics, medical research, and autonomous vehicles are some of the applications that emerged from AI development.
Government interest in AI has picked up in recent years as many government departments started to invest in AI in the form of pilot programs for various AI-based applications. AI adoption acts as a lever for transformational change in the way government services are conceived, designed, delivered, and consumed. It helps the government to provide integrated services to its citizens through the seamless flow of information across government departments. In addition, the adoption of AI helps in redesigning government processes, frees up staff, increases productivity, and improves citizen interactions.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, over 50% of government agencies will have modernized critical core legacy applications to improve resilience and agility.
An analysis by Markets and Markets indicates that the market size of artificial intelligence in the military is expected to reach USD 18.82 billion by 2025.
Gartner predicts that by 2024, 60% of government AI and data analytics investments aim to directly impact real-time operational decisions and outcomes.
According to Forbes, chatbots are AI-powered applications that we will see more of in 2022 as governments and authorities look for ways to automate public services.
AI Adoption Strategy in Government Services
The government is considered a large enterprise. Each department acts as an enterprise by itself. The main strategy of each government department is to transform each department into an AI Enterprise.
An AI strategy for the government is to define an AI vision, mission, and objectives that line up with government authoritative targets and devise a methodology for managing AI capability across the government.
The following diagram depicts the AI Strategy for any government. AI helps to transform government processes for citizens, improve service and enhance mission outcomes.
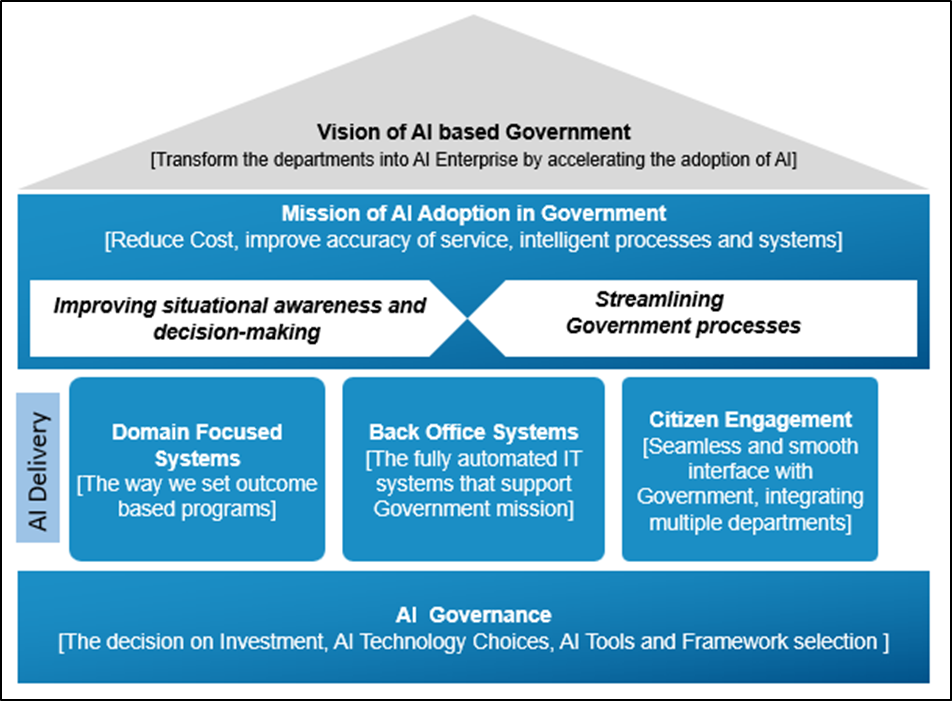
AI Adoption Strategy for Government
The vision of AI-based government is to transform the departments into AI enterprises by accelerating the adoption of AI.
The mission is to establish Intelligent systems that improve the delivery of service to citizens, accuracy in citizen service, and reduce the cost.
AI delivery can be broadly classified into 3 types of applications:
- Domain focused systems, helping to identify the patterns or develop predications
- Back office systems, built on intelligent automation tools called Robotic Process Automation
- Citizen engagement systems, which help directly to interact with citizens, employees, or any other stakeholders
Governments need to establish coordinating agencies and working groups to govern AI. AI governance covers the decision on investment, creation of ethics, and privacy framework, identification and usage of AI toolkit, and framework selection. It also decides on the nature of AI-skilled teams that are required and how to develop them to achieve the mission of government.
AI Governance Teams need to advise the government on how data-driven technologies are governed, help regulators support responsible innovation, and build a trustworthy system of governance. The governance team needs to establish policies to encourage the development of AI in a fair, transparent, and explainable manner.
Drivers for AI Adoption in Government
The following are the drivers for AI adoption in government:
Citizen Demands and Expectations
AI can support critical citizen capabilities. These include improving situational awareness and decision-making.
Modernize the Citizen Services
Citizen-facing applications improve the quality of services governments deliver to citizens.
For example, AI can improve patient outcomes by analyzing individual patient information to personalized treatment.
Innovation in Government Services
By automating simple, well-defined tasks, AI streamlines operations and augments the workforce. Employees can then spend more time on decisions that require human input.
For example, the usage of a computer-generated virtual assistant can reduce time spent replying to basic inquiries, while predictive analytics enables more informed decision-making.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Governments are collecting an abundant amount of data every day. Without an accurate analysis, data is not adequate for actionable insights. Better decision-making has the potential to both improve services and save time.
For example, AI can enhance the user experience for passengers by using historical and real-time data to predict demand and ensure that services are always available at the right time.
Improve Operational Efficiency
Automation of government employee tasks leads to saving of cost, time, and effort.
Types of AI for Government Operations
The key business and technology enablers of government services are:
- Social Collaborative Governance
- Digital Inclusion
- Mobility
- Contact Centre
- Cloud
- Integrated Government
- Data Analytics
- Open Data
- Certificate Less Governance System
- Security
- Internet of Things
- Interoperability
- Gamification
- Smart City
These can be better enabled by linking to AI adoption for better citizen services delivery.
The most commonly used AI technologies include:
- Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- Robotics
- Computer Vision
- Speech Recognition
- Image recognition
- Rule-based systems
- Predictive Analytics
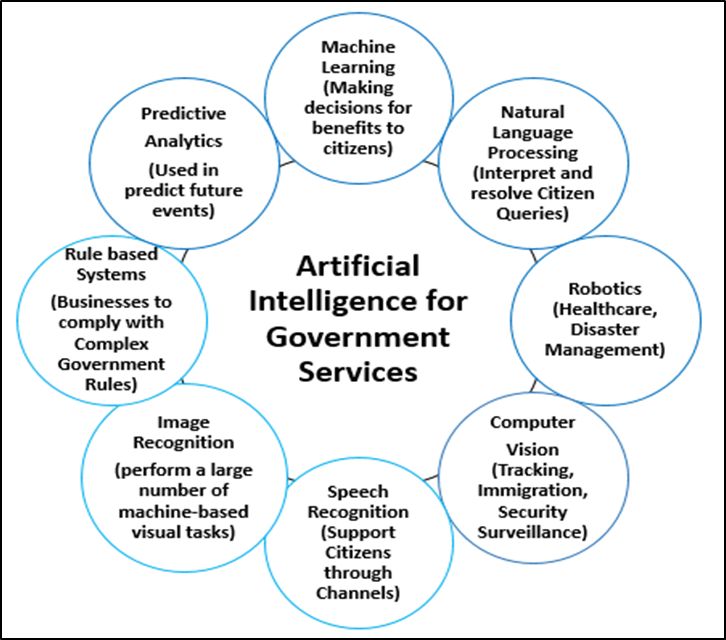
Types of AI for Government Services
AI-Enabled Government Reference Architecture
This section covers high-level AI-enabled government reference architecture, including terminology used, and application architecture. The main objective is to propose a framework for the e-Governance AI platform in order to handle real-time reporting from a large set of government data. This data may be taken from single or multiple applications; primarily those that are storing data in various repositories and various data stores across the departments and agencies.
The following diagram shows high-level AI-based government reference architecture with key components and layers. A brief description of these components and layers is provided in this section.
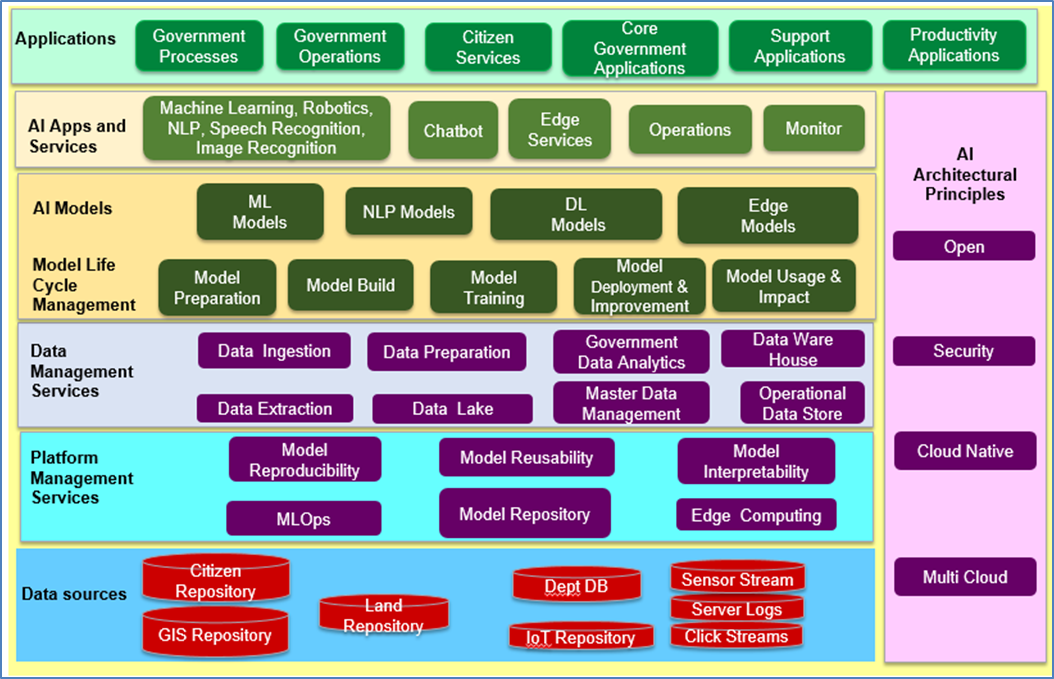
High-level reference architecture of Government AI platform
Data Sources
The data sources provide the insight required to solve the business problem. The data sources are structured, semi-structured, and unstructured, and come from many sources. AI-based solutions shall support the processing of all types of data from a variety of sources.
Category |
Internal |
External |
Structure |
Departmental Database, Data repositories, Data Warehouse, Data Marts |
Agency data Other Government data |
Semi/Unstructured |
e-Mails, Documents, XML documents |
Sensor Data, Log Stream Data, Web sites, Satellite Data, Social media, Bioinformatics , Blogs/Articles Documents, E-mails, Audio-visuals, Stream data and Web Analytics data |
Platform Management Services
Platform Management Services perform the model governance activities to ensure the model reproducibility, model reusability, and ensure model retraining/rollback as required. MLOps helps to automate and scale the deployment as well as manage the ML applications in production environments.
Data Management Services, Policies, processes, practices, and technologies are used to manage data from source to destination.
- Data Ingestion: This provides the capability to hold and transmit raw data collected from various sources to data. Stream extraction, parsing, and loading of the data are each done during this stage.
- Data Preparation: This service provides the mechanism to process different types of data and provide quick insights into the data.
- Data Lake: This has the capabilities required to make things easy for AI developers, data scientists, and analysts to store data of any size, shape, and speed, as well as perform all types of processing and analytics. It stores all data while making it faster to get up and running with batch, streaming, and interactive analytics.
- Data Warehouse: A government data warehouse stores whole government data, comprising of structured data from departmental database and data repository. The data warehouse supports massively parallel processing and share-nothing architecture, and provides optimal performance considering structured and unstructured data. It is designed in such a way that it has no single point of failure.
AI Models help in processing various use-cases and identification of the right model to fulfill the business outcome. Various models that can be developed based on the use-cases are ML Models, NLP Models, DL Models, and Edge Models.
- Model Preparation and Build: AI-intelligent agents and techniques help in model preparation and model construction. Evaluation helps in the identification of the best model in terms of specifications. Testing and self-healing are performed during the execution service.
- Train the model with different hyperparameters to maximize the performance.
- During the model deployment and improvement step, not only does the deployment process automate, but also performs the process of continuous retraining and redeployment, model integration with operational workflows, and integration of operational feedback for model improvement.
- Model usage and impact: The function of this component is to ensure that the AI models are actually used by the lines of businesses and that they are affecting business outcomes.
AI Apps and Services cover the various types of AI components to enhance citizen services. The various AI services are ML services, NLP services, Robotic Services, Edge services. Generally, these services are modeled as Microservices. A pipeline is built to ingest the input the data, run the AI model with that input, and store the output in a database. These AI services are developed as Microservices.
The application layer consists of government processes, core government applications, support applications, and productivity applications. Different users may want different types of outputs based on their roles, responsibilities, and functions. It is responsible to present the appropriate services using autonomous intelligent agents that coordinate and manage the application services to meet the citizens’ needs.
Benefits of AI for Government
AI can be used to assist the public to interact with the government and access citizen services. AI can speed up existing tasks and perform jobs beyond human ability.
AI also can help with automating government interactions, most of which currently rely on humans. With AI, emails, online chat, calls, responses to queries, social media chat and more can all be automated and, to provide a much better customer experience, the AI systems store previous government interactions, using them for analysis.
Real-time assistance to citizens is most useful for government officials that are in constant contact with citizens under tight time restraints. This includes disaster management systems where citizens need to be aware of real-time calamity status and weather forecasts.
Data mining and cloud-based AI allows for large quantities of data to be analyzed and processed, giving governments much better insight into their citizens and government processes which, in turn, allows them to make much better business decisions.
In regards to predictive power, AI-based systems help in processing large amounts of data quickly. This helps in the reduction of wait times, fewer errors, and faster emergency responses. It also helps create deeper insights and better citizen experiences.
Other benefits of usage of AI in Government are:
- To provide insights into how government schemes and policies are performing, and why (descriptive and causal analyses)
- Design of better schemes and projects by being more citizen-centric and effective
- To determine likely future scenarios and recommend best courses of action (predictive and prescriptive analyses)
- To gauge sentiments of people of the government, and understand their perceptions of and attitudes towards government policies
- To enhance the effectiveness of regulatory and tax collection systems of the government
- Enhanced citizen satisfaction through participation in decision-making
- Formulation of the right policies that factor the needs of the people
Use Cases of AI in Government
The following are the brief description and use cases of AI usage in government services across multiple departments.
Agriculture
Agriculture is an area that requires various resources, labor, money, and time for the best results. Today, agriculture is becoming digital, and AI is emerging in this field. AI in agriculture can be very helpful for farmers and is being applied to agriculture robotics, solid and crop monitoring, and predictive analysis. Some of the high-level use cases of AI in agriculture are as follows:
- Provides real-time information to farmers on parameters affecting crop cultivation (rainfall, soil quality) and expert advice on how to maximize yield given the parameters
- GIS and sensor-based technologies to capture and transmit geography-wise data on soil and weather conditions in real-time; soil health monitoring and restoration
- Analysis of trends of cropped areas; economics of various crops area-wise over the last 5 years; the demand-supply position for different agricultural produce across the country; to arrive at the optimized crop area planning for various crops in different agro-climatic regions of the government; giving decision support to agricultural planners
- Mobile-based technologies to disseminate expert advice, warnings, advisories, crop demand and prices, and other key information to farming communities
- Advanced detection of pest attacks
- Prediction of crop prices to inform sowing practices
Healthcare
The healthcare domain is applying AI to make a better and faster diagnosis than humans. AI can help doctors with diagnoses and can inform when patients are worsening so that medical help can reach the patient before hospitalization. Some of the use cases of AI in healthcare are:
- AI-driven diagnostics, such as imaging diagnostics
- Personalized treatment for the patients; analysis of patient data to predict patients’ risk scores so that doctors can prioritize
- Identification of potential pandemics and tracking of the spread; cross-checks patients with similar symptoms from different locations; detection of patterns; warning of when an outbreak might occur
- Disease trends based on demographic and social parameters
- Identify contacts with a known carrier of the virus
- Integrating climatic, economic, and social data along with the quality of healthcare provided; identifying geographic regions that are vulnerable to viral diseases; providing decision support to the department (real-time)
Education
AI can automate grading so that the tutor can have more time to teach. AI chatbots can communicate with students as teaching assistants. AI can work as a personal virtual tutor for students, which will be accessible easily at any time and any place. Some of the use cases of AI in education are:
- Adaptive learning tools for customized learning
- Intelligent and interactive tutoring systems
- Provide personalized education regardless of the number of students
- Predictive tools to inform pre-emptive action for students predicted to drop out of school
- Analyze students’ progress and find inconsistencies; review students work to identify strengths and recommend revisions
- Automated rationalization of teachers
GIS and Disaster Management
AI has been leveraged by governments for disaster management and early warnings on calamity. Artificially intelligent systems, when fed with data about thousands of previous disasters, can accurately predict the future relating to the disasters that might occur. Some of the use cases of the AI are:
- Help in analyzing GIS data on natural resources management, natural disasters
- Map the dryness of forests to predict wildfire better
- Predict a disaster and identify the areas likely to be affected; suggest advance interventions required to mitigate the adverse impact on the population
Smart City
AI is used in smart city concepts such as safe city, smart water, smart transport, smart waste, smart parking, and smart traffic. Some of the use cases are:
- Predicting fire risk in buildings; develop AI software aimed at identifying buildings that have a higher likelihood of fire incidents
- Smart waste, a continual inspection of sewer pipes leads to higher cost. AI solution to optimize the path and reduce the cost
- Smart homes and smart public facilities
- Crowd management
- AI-driven service delivery
Revenue
The revenue domain is implementing automation, chatbot, adaptive intelligence, algorithm trading, and machine learning into financial processes. Some of the use cases on the usage of AI are:
- Finding gaps between projected revenue and actuals
- Helping to increase government revenue
- Identifying tax evaders, leakages of taxes, and other major revenues; conducting causal analysis; providing decision support
Public Relations System
AI can assist with analyzing the text inputs (unstructured data) in the public relations system and the popular print media, identifying key problem areas (i.e., region, type of problem, frequency, severity), and suggesting suitable remedial action. Chatbots are the most commonly used in government services. Some of the use cases on the usage of AI are:
- Scheduling meetings
- Answering FAQs
- Directing requests to the appropriate area within the government
- Filling out forms
- Assisting with searching documents
- Designing a happiness Index, appropriate to the socio-economic profile of the government agency; supporting the government in conducting appropriate sample surveys; analyzing the results; making suitable recommendations for enhancement of the Index
Transportation
AI-based systems can help transportation services providers optimize route planning and delivery schedules. Some of the use cases are,
- Automated Traffic control; AI to optimize the traffic systems toward reduced travel times; reduced number of traffic stops; reduced wait times
- Autonomous trucking
- Intelligent transportation systems to monitor the condition of the roads and provide advance recommendations on optimal resource utilization for producing the best impact on taxpayers
- Community-based parking
- Route flow optimization
Public Safety
AI can help to ensure public safety when they use their services. For example, real-time crime tracking can help keep citizens safe when they use public transport in urbanized areas. Some of the AI use cases are,
- Used to identify patterns in policing heat maps to forecast where and when next crimes are likely to occur
- To identify optimal police patrol presence. Police are able to place resources where they are needed, increase efficiency and ensure regular patrols protect the public.
- Automate emergency call lines by understanding and categorizing queries
- To find the missing children, AI helps to provide the tips for suspicious online activity and share the information to concern authorities
Security
The following are high level use cases of AI to be used in security domain,
- To improve the nautical, terrain, and aeronautical charting, which helps to enable safe and precise navigation and better surveillance
- Increase the safety of equipment like aircraft, ships and vehicles in dangerous situations
- Predict the parts failure, automating diagnosis and planning maintenance
Conclusion
With the recent advances in AI and deep learning technologies, more government agencies are starting to use AI technologies to improve their systems and services. The use of AI in government must take into account privacy and security, compatibility with legacy systems, and evolving workloads.
AI adoption acts as a lever for transformational change in the way government services are conceived, designed, delivered, and consumed. It helps the government to provide integrated services to its citizens through the seamless flow of information across government departments. In addition, the adoption of AI helps in redesigning government processes, to free up staff, increasing productivity, or improving citizen interactions.
AI and ML models provide better transparency and accuracy of the services to the citizens. AI helps in better operational efficiency resulting in cost savings to the government, improved services to the citizens, and data-driven decision making that leads to better service to citizens.
AI-based government reference architecture supports AI solutions with robustness, speed to market, and business outcomes.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Vijayasimha Alilughatta and Raju Alluri of Wipro Digital Architecture Practice/Wipro Ltd for giving the required time and support in many ways throughout the writing of this article.

