Android Software Stack and Terminology (Tutorial 01)
The Android system software stack is typically divided into the four areas as the following graphic:
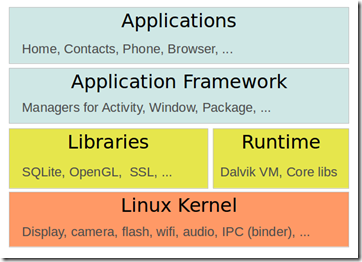
Terminology
- Android Software Development Kit (Android SDK) contains the necessary tools to create, compile and package Android applications
- Android debug bridge (adb), which is a tool that allows you to connect to a virtual or real Android device
- Google provides two integrated development environments (IDEs) to develop new applications.
- Android Developer Tools (ADT) are based on the Eclipse IDE
- Android Studio based on the IntelliJ IDE
- Android RunTime (ART) uses Ahead Of Time compilation, and optional runtime for Android 4.4
- Android Virtual Device (AVD) - The Android SDK contains an Android device emulator. This emulator can be used to run an Android Virtual Device (AVD), which emulates a real Android phone
- Dalvik Virtual Machine (Dalvik)-
- The Android system uses a special virtual machine, Dalvik, to run Java-based applications. Dalvik uses a custom bytecode format which is different from Java bytecode.
- Therefore you cannot run Java class files on Android directly; they need to be converted into the Dalvik bytecode format.


