Using CockroachDB CDC With Azure Event Hubs
Previous Articles on CockroachDB CDC
- Using CockroachDB CDC with Confluent Cloud Kafka and Schema Registry
- SaaS Galore: Integrating CockroachDB With Confluent Kafka, Fivetran, and Snowflake
- CockroachDB CDC Using Minio as Cloud Storage Sink
- CockroachDB CDC With Hadoop Ozone S3 Gateway and Docker Compose
Motivation
Azure Event Hubs is a critical part of the Azure ecosystem. We're in the early stages of adopting Azure and while we focus on the official integration, I'd like to provide workarounds in the meantime.
This tutorial is using enterprise changefeeds: you will need an enterprise license, access to a CockroachDB dedicated cluster, or enable billing in your CockroachDB Serverless cluster to activate enterprise features like CDC to Kafka.
High-Level Steps
- Deploy Azure Event Hubs
- Deploy a CockroachDB cluster with enterprise changefeeds
- Verify
Step-By-Step Instructions
Deploy Azure Event Hubs
You will need an Azure Event Hubs account. You can sign up for a free account.
Once you're done, follow the steps outlined in this quickstart to create an instance of Azure Event Hubs.
High-level steps:
- Create a resource group
- Create an Event Hub Namespace
- Create an Event Hub
- Add a SAS policy to an Event Hub
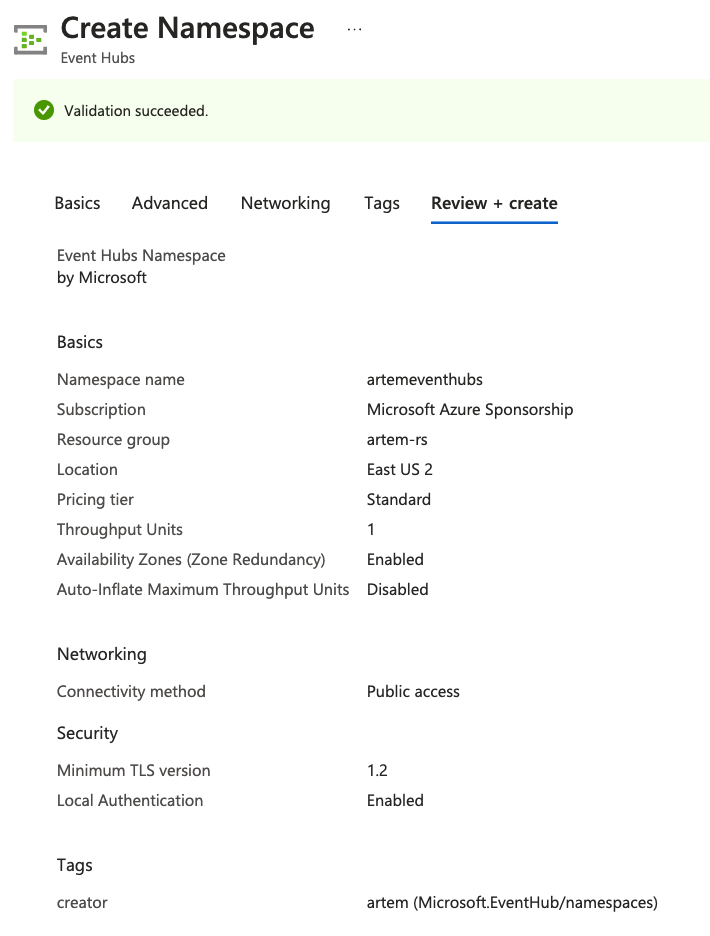
Once complete, create the deployment:
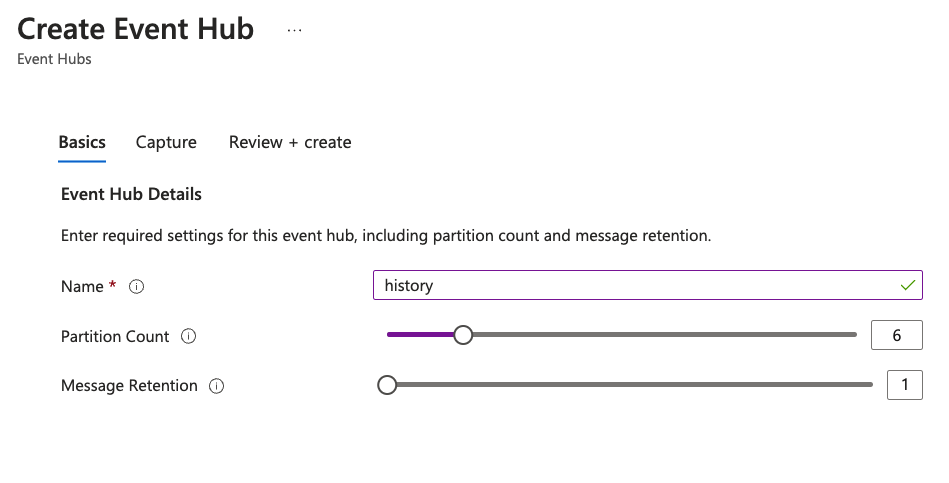
The steps are equivalent to creating topics in Kafka. For example:
confluent kafka topic create stock --partitions 6 confluent kafka topic create history --partitions 6
I ended up with an Event Hubs namespace called artemeventhubs and Event Hubs named stock and history.
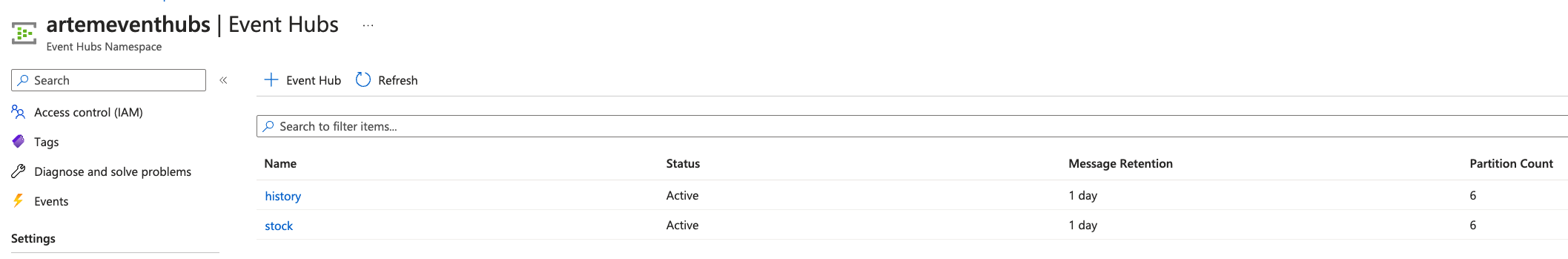
Once created, you need a SAS Policy to access your Event Hubs:
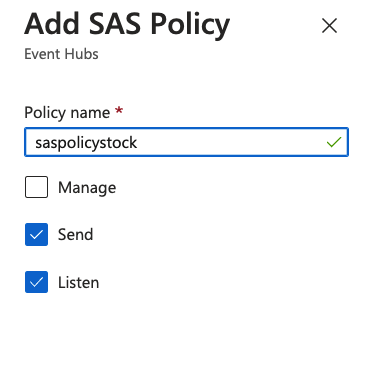
Capture the SAS policy details, as we will need that for the next step. You need to click on the SAS policy to open the details dialog. As of now, it seems every Event Hub has its own associated SAS policy. If I figure out a way to use the same policy for more than one topic, I will highlight it.
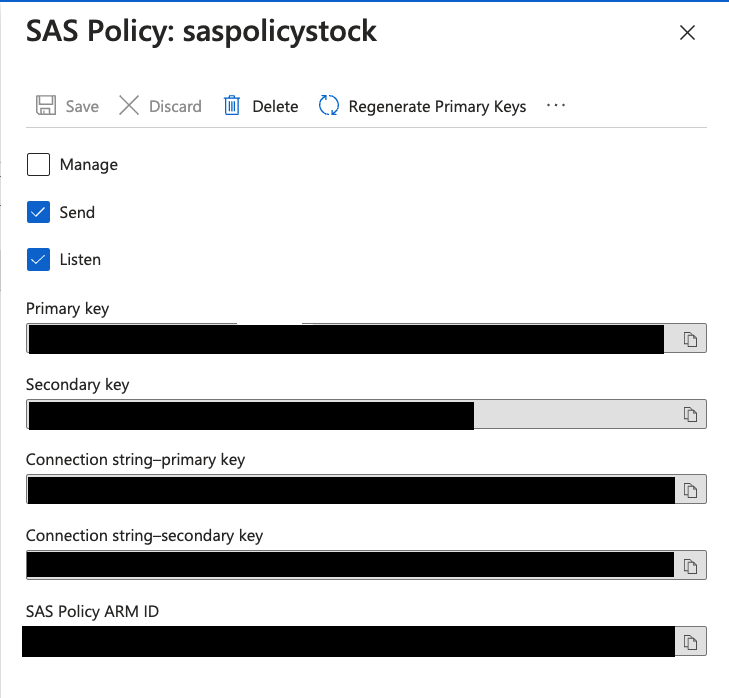
In the SAS Policy Details, capture the "Connection string-primary key."
Endpoint=sb://artemeventhubs.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=saspolicytpcc;SharedAccessKey=<REDACTED>;EntityPath=history
Deploy a CockroachDB Cluster With Enterprise Changefeeds
You can spin up a dedicated cluster using the following directions. My cluster is a 3-node cluster in AWS with AZ failure tolerance in us-east-1.
To enable CDC we need to execute the following command:
SET CLUSTER SETTING kv.rangefeed.enabled = true;
Event Hubs supports Kafka protocol with port 9093. We can use the connection string URL from the SAS policy and protocol kafka://. The equivalent of kafka://<confluent cloud kafka endpoint url>:9092 in Event Hubs is kafka://artemeventhubs.servicebus.windows.net:9093. The sasl_user and sasl_password section is where it gets tricky. I owe a huge thanks to the article "How to Use Kafka Client with Azure Event Hubs" for providing answers for the associated fields. sasl_user will be set to $ConnectionString just as the article says. sasl_password however, is a bit tricky. Considering CockroachDB expects a URL-encoded secret key, it took me several tries before I got it right. The trick is to URL-encode the entire connection string from the SAS Policy. I'm consistently relying on the following URL-encoder service to URL-encode these values.
Create a Changefeed With the Event Hubs Information
CREATE CHANGEFEED FOR TABLE history INTO "kafka://artemeventhubs.servicebus.windows.net:9093?tls_enabled=true&sasl_enabled=true&sasl_user=$ConnectionString&sasl_password=Endpoint%3Dsb%3A%2F%2Fartemeventhubs.servicebus.windows.net%2F%3BSharedAccessKeyName%3Dsaspolicytpcc%3BSharedAccessKey<REDACTED>EntityPath%3Dhistory&sasl_mechanism=PLAIN" WITH updated, format = json;
job_id ---------------------- 801162005835612162 (1 row) NOTICE: changefeed will emit to topic history Time: 235ms total (execution 215ms / network 20ms)
The only thing that remains is generating a workload. We are going to use the TPC-C workload bundled with the Cockroach binary. In a new terminal window, run the following two commands:
Generate Sample Data
cockroach workload fixtures import tpcc --warehouses=10 "postgresql://<user>@<Cockroach Cloud Dedicated url>:26257/tpcc?sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=/path/certs/cluster-ca.crt"
Execute the Workload
cockroach workload run tpcc --warehouses=10 --ramp=3m --duration=1h "postgresql://<user>@<Cockroach Cloud Dedicated url>:26257/tpcc?sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=/path/certs/cluster-ca.crt"
Verify
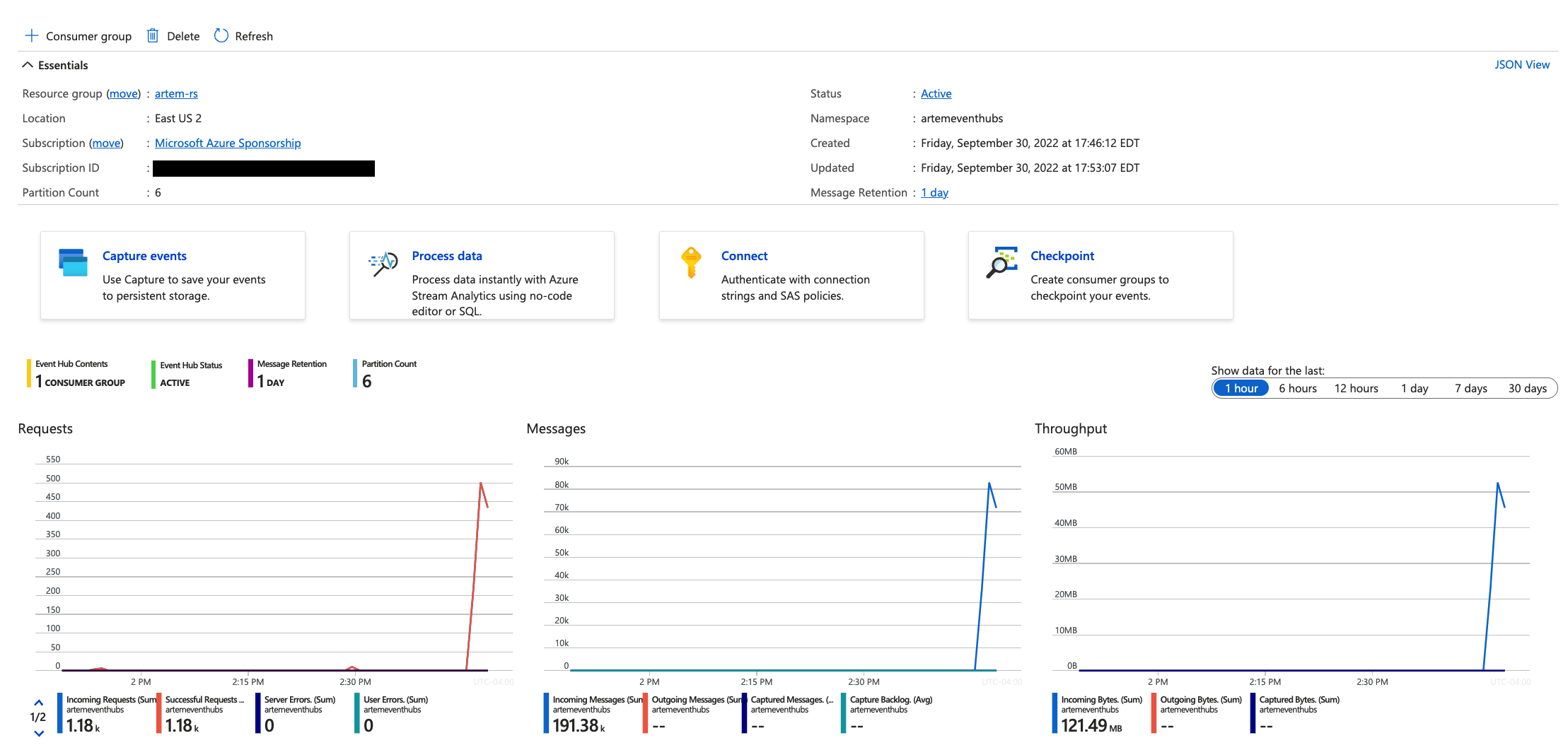
The only thing that's left is to confirm the messages are sent to Azure Event Hubs. In the Azure Console, navigate to the individual Event Hubs. You can see the changing message counters:
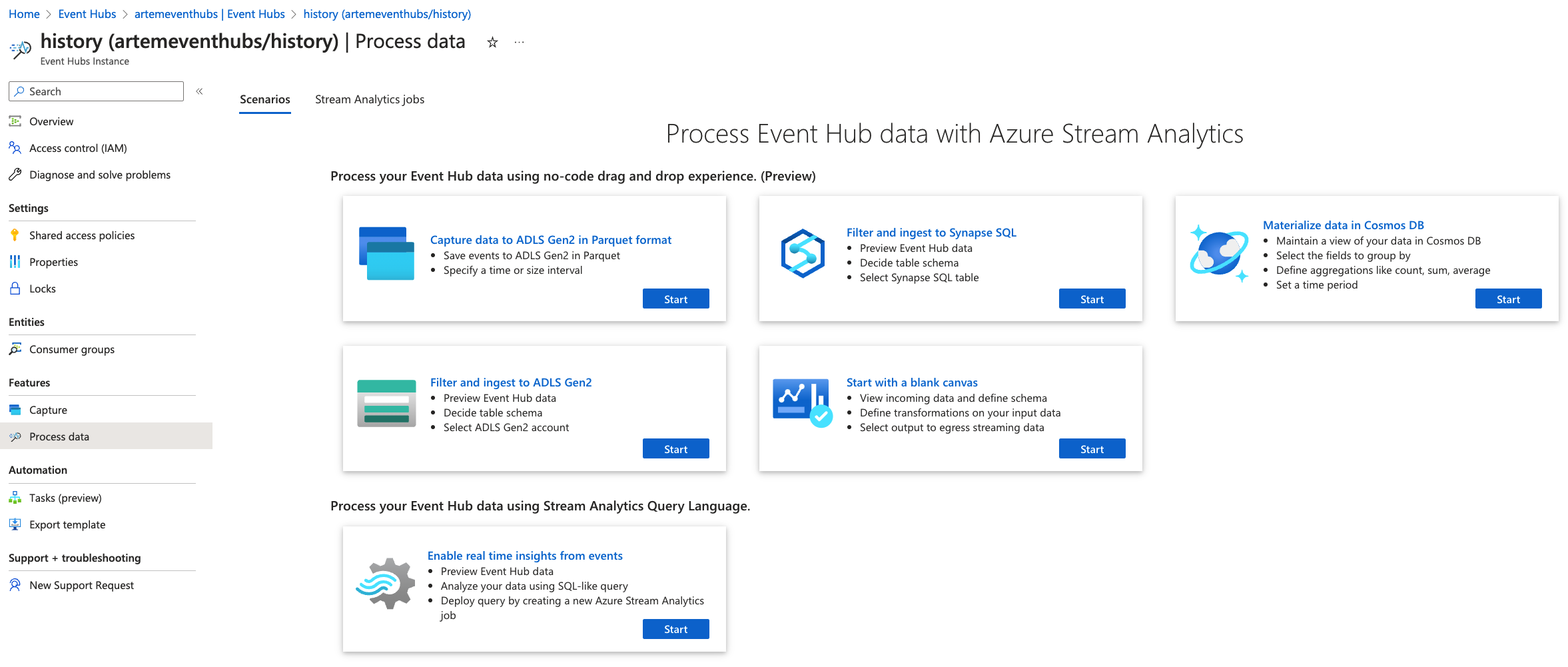
The simplest way to view messages in the Event Hubs is to click the "Process data" option on the Event Hub page, then select the "Enable real-time insights from events" option.
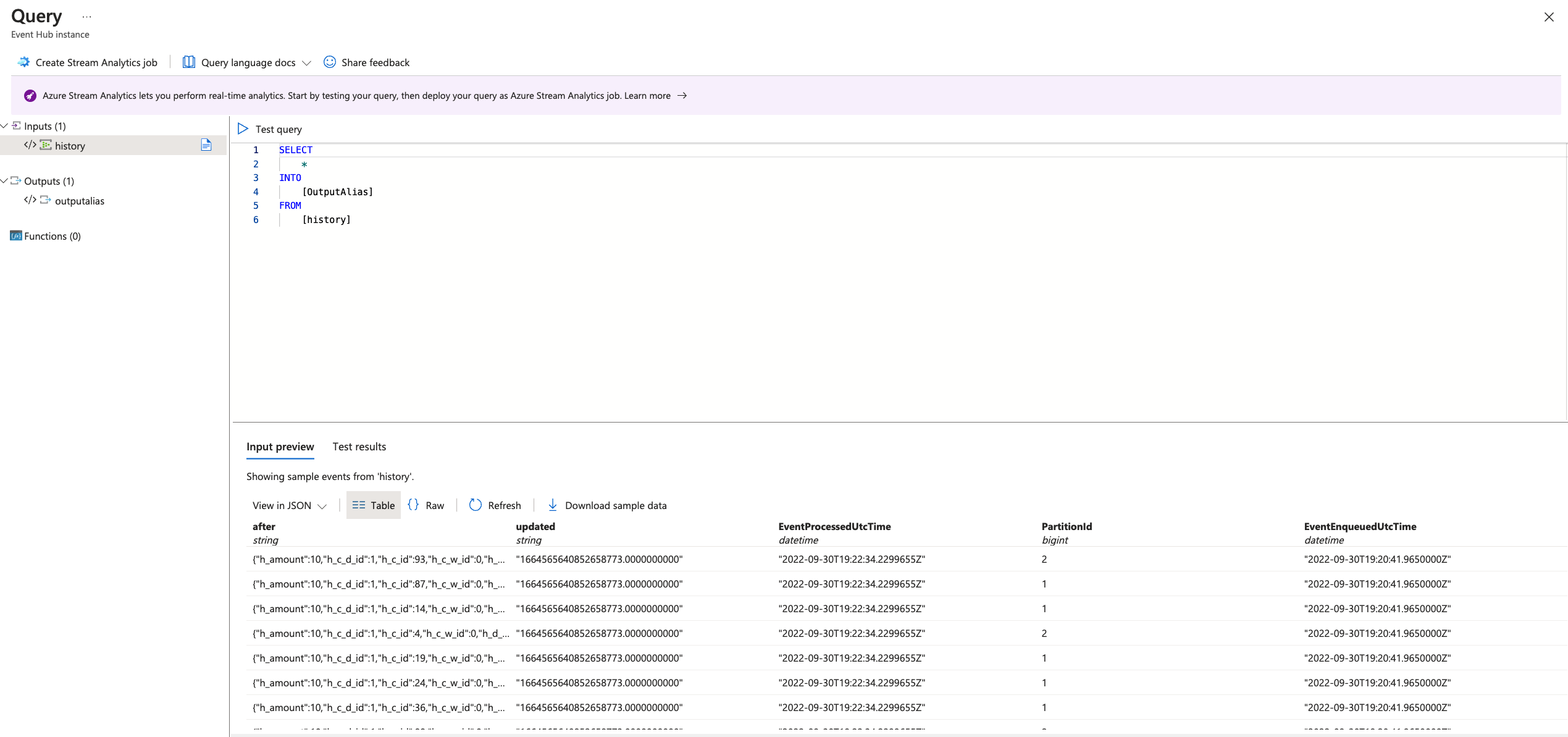
There, an SQL Editor window will open and load messages:
And this is how you can leverage existing CockroachDB capability with non-standard services like Azure Event Hubs. Hopefully, you've found this a viable solution until Event Hubs is a first-class citizen in CockroachDB.

