DevOps and Automation
In the rapidly changing world of technology, DevOps is the vehicle that propels software development forward, making it agile, cost-effective, fast, and productive. This article focuses on key DevOps tools and practices, delving into the transformative power of technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes. By investigating them, I hope to shed light on what it takes to streamline processes from conception to deployment and ensure high product quality in a competitive technological race.
Understanding DevOps
DevOps is a software development methodology that bridges the development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams in order to increase productivity and shorten development cycles. It is founded on principles such as continuous integration, process automation, and improving team collaboration.
Adopting DevOps breaks down silos and accelerates workflows, allowing for faster iterations and faster deployment of new features and fixes. This reduces time to market, increases efficiency in software development and deployment, and improves final product quality.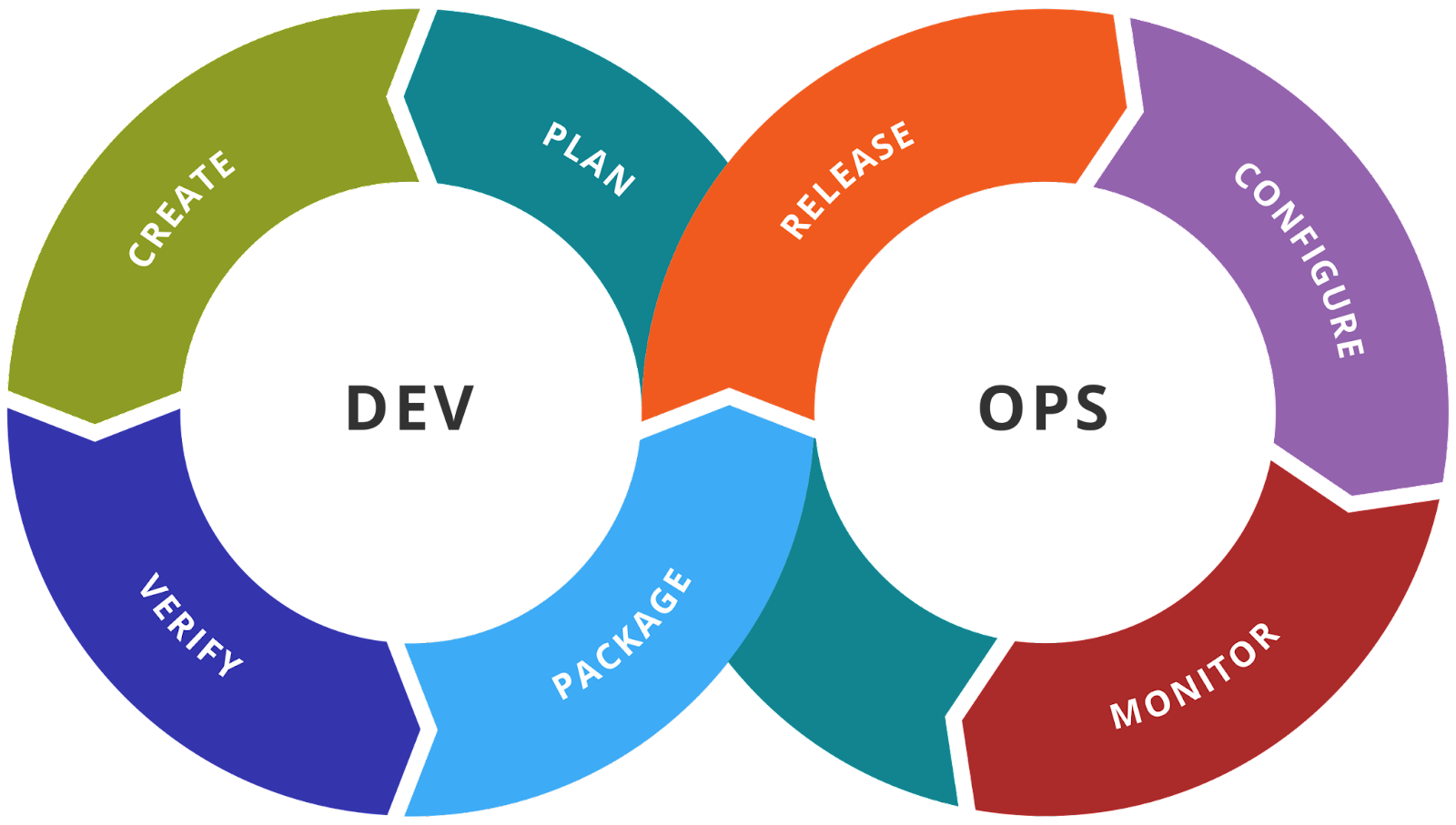
The Role of Automation in DevOps
In DevOps, automation is the foundation of software development and delivery process optimization. It involves using tools and technologies to automatically handle a wide range of routine tasks, such as code integration, testing, deployment, and infrastructure management.
Through automation, development teams get the ability to reduce human error, standardize processes, enable faster feedback and correction, improve scalability and efficiency, and bolster testing and quality assurance, eventually enhancing consistency and reliability.
Several companies have successfully leveraged automation:
- Walmart: The retail corporation has embraced automation in order to gain ground on its retail rival, Amazon. WalmartLabs, the company's innovation arm, has implemented OneOps cloud-based technology, which automates and accelerates application deployment. As a result, the company was able to quickly adapt to changing market demands and continuously optimize its operations and customer service.
- Etsy: The e-commerce platform fully automated its testing and deployment processes, resulting in fewer disruptions and an enhanced user experience. Its pipeline stipulates that Etsy developers first run 4,500 unit tests, spending less than a minute on it, before checking the code into run and 7,000 automated tests. The whole process takes no more than 11 minutes to complete. These cases demonstrate how automation in DevOps not only accelerates development but also ensures stable and efficient product delivery.
Leveraging Docker for Containerization
Containerization, or packing an application's code with all of the files and libraries needed to run quickly and easily on any infrastructure, is one of today's most important software development processes. The leading platform that offers a comprehensive set of tools and services for containerization is Docker. It has several advantages for containerization in the DevOps pipeline:
- Isolation: Docker containers encapsulate an application and its dependencies, ensuring consistent operation across different computing environments.
- Efficiency: Containers are lightweight, reducing overhead and improving resource utilization when compared to traditional virtual machines.
- Portability: Docker containers allow applications to be easily moved between systems and cloud environments.
 Many prominent corporations leverage Docker tools and services to optimize their development cycles. Here are some examples:
Many prominent corporations leverage Docker tools and services to optimize their development cycles. Here are some examples:
PayPal: The renowned online payment system embraced Docker for app development, migrating 700+ applications to Docker Enterprise and running over 200,000 containers. As a result, the company's productivity in developing, testing, and deploying applications increased by 50%.
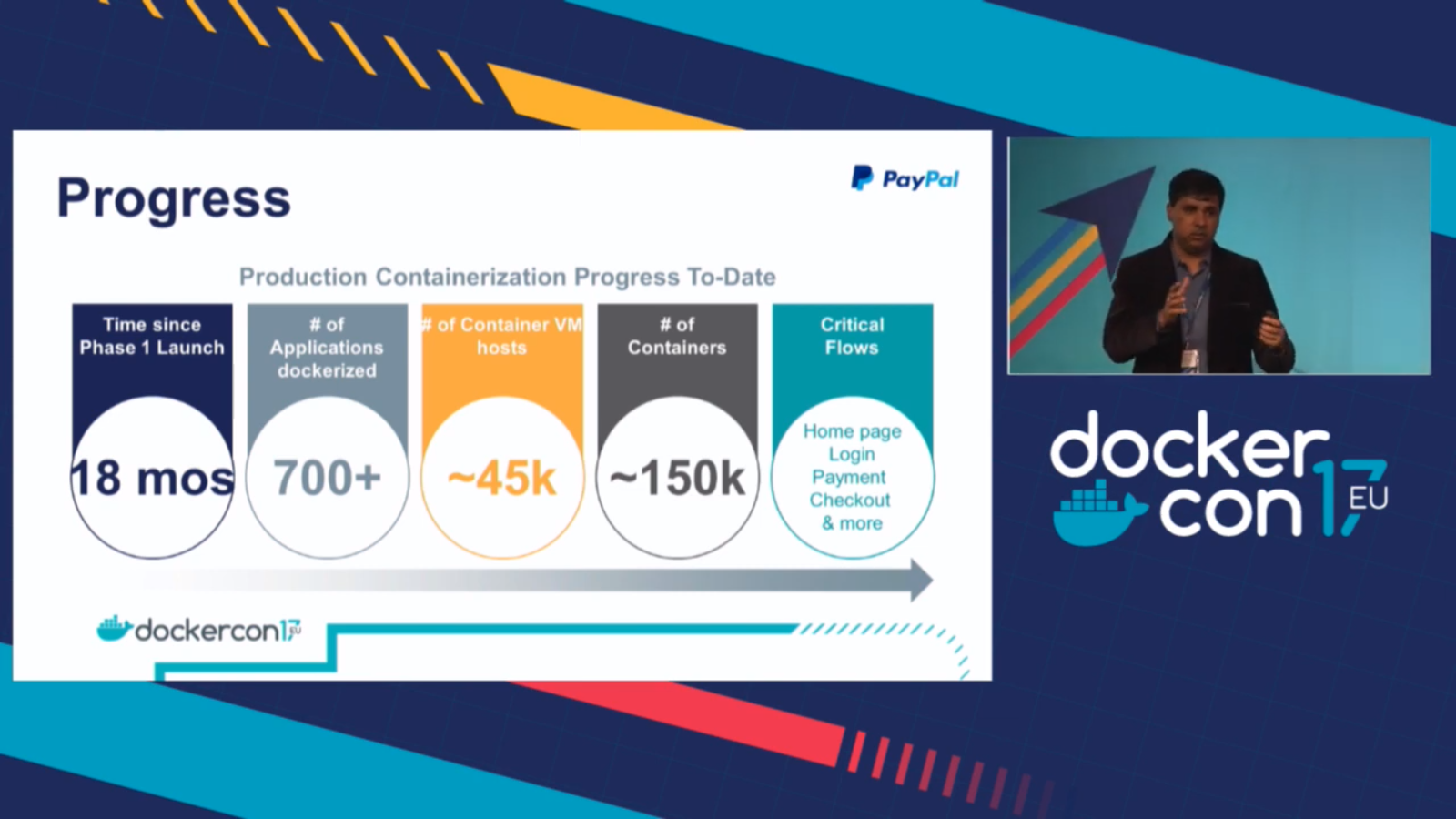
- Visa: The global digital payment technology company used Docker to accelerate application development and testing by standardizing environments and streamlining operations. The Docker-based platform assisted in the processing of 100,000 transactions per day across multiple global regions six months after its implementation.

Orchestrating Containers With Kubernetes
Managing complex containerized applications is a difficult task that necessitates the use of a specialized tool. Kubernetes (aka K8S), an open-source container orchestration system, is one of the most popular. It organises the containers that comprise an application into logical units to facilitate management and discovery. It then automates application container distribution and scheduling across a cluster of machines, ensuring resource efficiency and high availability.
Kubernetes enables easy and dynamic adjustment of application workloads, accommodating changes in demand without requiring manual intervention. This orchestration system streamlines complex tasks, allowing for more consistent and manageable deployments while optimizing resource utilization.
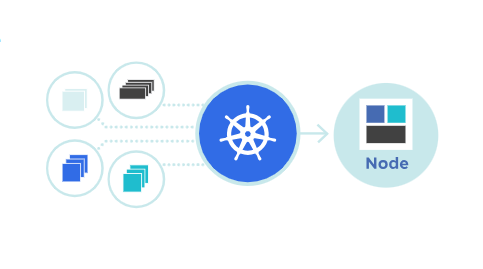
Setting up a Kubernetes cluster entails installing Kubernetes on a set of machines, configuring networking for pods (containers), and deploying applications using Kubernetes manifests or helm charts. This procedure creates a stable environment in which applications can be easily scaled, updated, and maintained.
Automating Development Workflows
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are critical components of DevOps software development. CI is the practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple contributors into a single software project. It is typically implemented in such a way that it triggers an automated build with testing, with the goals of quickly detecting and fixing bugs, improving software quality, and reducing release time.
After the build stage, CD extends CI by automatically deploying all code changes to a testing and/or production environment. This means that, in addition to automated testing, the release process is also automated, allowing for a more efficient and streamlined path to delivering new features and updates to users.
Docker and Kubernetes are frequently used to improve efficiency and consistency in CI/CD workflows. The code is first built into a Docker container, which is then pushed to a registry in the CI stage. During the CD stage, Kubernetes retrieves the Docker container from the registry and deploys it to the appropriate environment, whether testing, staging, or production. This procedure automates deployment and ensures that the application runs consistently across all environments.
Many businesses use DevOps tools to automate development cycles. Among them are:
- Siemens: The German multinational technology conglomerate uses GitLab's integration with Kubernetes to set up new machines in minutes. This improves software development and deployment efficiency, resulting in faster time-to-market for their products and cost savings for the company.
- Shopify: The Canadian e-commerce giant chose Buildkite to power its continuous integration (CI) systems due to its flexibility and ability to be used in the company's own infrastructure. Buildkite allows lightweight Buildkite agents to run in a variety of environments and is compatible with all major operating systems.
Ensuring Security in DevOps Automation
Lack of security in DevOps can lead to serious consequences such as data breaches, where vulnerabilities in software expose sensitive information to hackers. This can not only result in operational disruptions like system outages significantly increasing post-deployment costs but also lead to legal repercussions linked to compliance violations. Integrating security measures into the development process is thus crucial to avoid these risks. The best practices for ensuring security involve:
- In the case of Docker containers, using official images, scanning for vulnerabilities, implementing least privilege principles, and regularly updating containers are crucial for enhancing security.
- For Kubernetes clusters, it is essential to configure role-based access controls, enable network policies, and use namespace strategies to isolate resources.
Here are some examples of companies handling security issues:
- Capital One: The American bank holding company uses DevSecOps to automate security in its CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that security checks are integrated into every stage of software development and deployment.
- Adobe: The American multinational computer software company has integrated security into its DevOps culture. Adobe ensures that its software products meet stringent security standards by using automated tools for security testing and compliance monitoring.
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls
Implementing DevOps and automation frequently encounters common stumbling blocks, such as resistance to change, a lack of expertise, and integration issues with existing systems. To overcome these, clear communication, training, and demonstrating the value of DevOps to all stakeholders are required.
Here are some examples of how businesses overcame obstacles on their way to implementing DevOps methodology:
- HP: As a large established corporation, HP encountered a number of challenges in transitioning to DevOps, including organizational resistance to new development culture and tools. It relied on a "trust-based culture and a strong set of tools and processes" while taking a gradual transition approach. It started with small projects and scaled up, eventually demonstrating success in overcoming skepticism.
- Target: While integrating new DevOps practices, the US's seventh-largest retailer had to deal with organizational silos and technology debt accumulated over 50 years in business. It introduced a set of integration APIs that broke down departmental silos while fostering a learning and experimentation culture. They gradually improved their processes over time, resulting in successful DevOps implementation.
The Future of DevOps and Automation
With AI and ML taking the world by storm, these new technologies are rapidly reshaping DevOps practices. In particular, they enable the adoption of more efficient decision-making and predictive analytics, significantly optimizing the development pipeline. They also automate tasks such as code reviews, testing, and anomaly detection, which increases the speed and reliability of continuous integration and deployment processes.
To prepare for the next evolution in DevOps, it's crucial to embrace trending technologies such as AI and machine learning and integrate them into your processes for enhanced automation and efficiency. This involves investing in training and upskilling teams to adapt to these new tools and methodologies. Adopting flexible architectures like microservices and leveraging data analytics for predictive insights will be key.
Conclusion
In this article, we have delved into the evolution of the approaches toward software development, with the DevOps methodology taking center stage in this process. DevOps is created for streamlining and optimizing development cycles through automation, containerization, and orchestration. To reach its objectives, DevOps uses powerful technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, which not only reshape traditional workflows but also ensure enhanced security and compliance. As we look towards the future, the integration of AI and ML within this realm promises further advancements, ensuring that DevOps continues to evolve, adapting to the ever-changing landscape of software development and deployment.
Additional Resources
Read on to learn more about this topic:
The official Docker documentation;
The official Kubernetes documentation;
"DevOps with Kubernetes";
"DevOps: Puppet, Docker, and Kubernetes";
"Introduction to DevOps with Kubernetes";
"Docker in Action".

