AWS Applications Deployment Basics: Setup NGINX
Introduction
In the previous post of this series "AWS Application Deployment Basics," we set up a PostgreSQL database and then we connect to it via a NodeJS application.
However, the Nodejs application is running on the same machine and database access is local for it. It is a totally valid setup and because it is on the same machine, the access is straightforward. But, having applications and databases running on separate machines is also a very common setup and we will cover that path as well later in this series. But today, we will focus mostly on the web server we want to run on an EC2 instance in the public subnet.
If you remember our VPC setup, we have a public EC2 instance as well, which we are currently using as a Bastian-server (a.k.a. jump host) and as a NAT instance well. Now, the idea here is to use it as an NGINX web server as well. This is an Amazon Linux EC2 instance.
Now in the real world, you might want to run NGINX on a separate EC2 instance, however, the process is the same, and just to save some time and cost I will just use the already running EC2 instance (public subnet) for this as well.
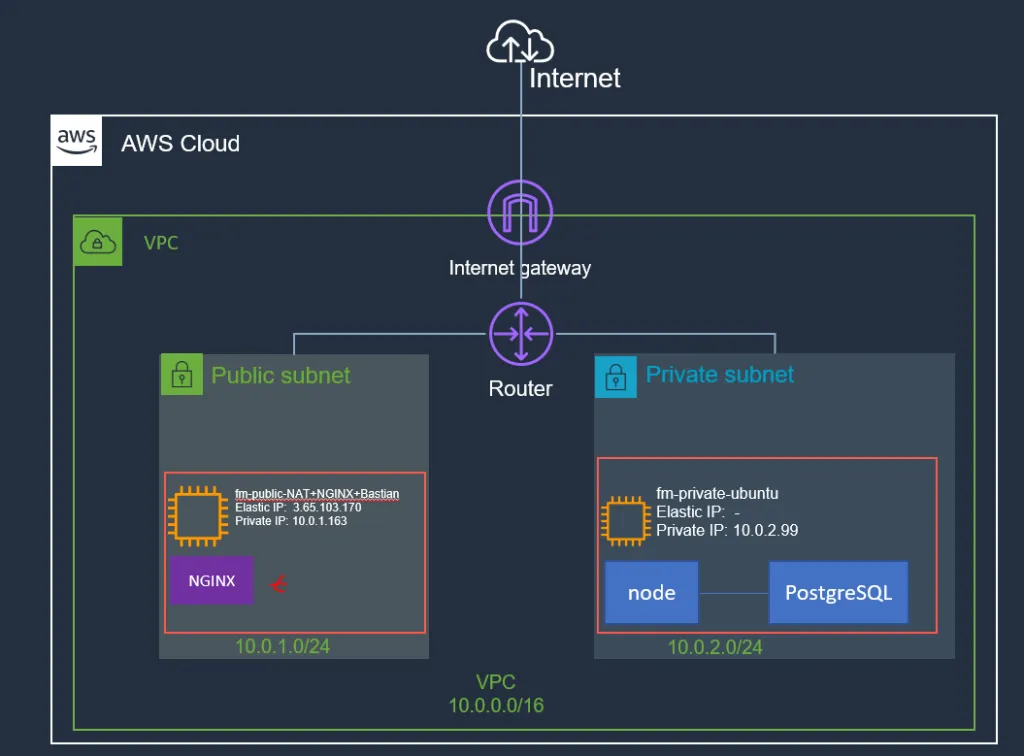
Architecture Diagram
Here is the updated diagram which shows the NGINX we will be setting up.
Installing NGINX on Amazon Linux EC2
1. SSH to Bastian Server (Public Amazon Linux EC2 Instance)
ssh -i ./fm-keypair.pem ec2-user@ip-address-machine //SSH to Bastian Server2. Update Packages on Amazon Linux
sudo yum update // (ubuntu) sudo apt-get update
3. Install NGINX on Amazon Linux
sudo yum install nginx // (Ubuntu) sudo apt-get install nginx4. Test Installation Using Bash
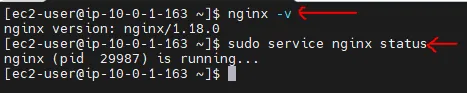
Cool. installation is done and let's do a small test to confirm that it is working.
nginx -vsudo service nginx status
Here is the output of action:
Accessing the Web Server
NGINX typically comes with a default website and config file which is configured to deliver the default website.
So, let’s try to access this website locally using curl:
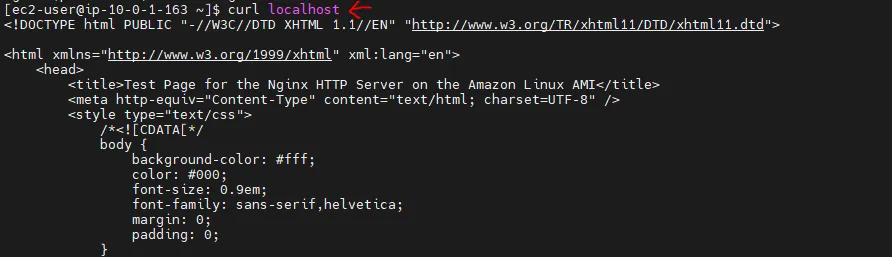
You can see that we received the HTML of the default website. Actually, if we see the security group we attached with this instance:

You can see the security group already have the Inbound HTTP rule configured and actually I can access this web page from anywhere in the world, let’s try to access it using Elastic-IP of Bastian-host (same EC2 with NGINX) in the web browser:

Connecting NGINX With Node.js Application
Let’s do a simple test. We will connect NGINX with Node.js application by using NGINX reverse proxy capability:
So, this way, we shall be able to get product data in PostgreSQL.
Prepare NodeJS Application
We will be using PM2 to run our Nodejs application. PM2 will keep running node server in the background.
Install PM2 on EC2 In The Private Subnet (Where NodeJS Application Is Running and Run App):
1. ssh to ubuntu EC22. sudo npm install pm2 -g // Install pm23. pm2 start server.js // Run the Server app
Here is the output:

Other relevant commands for pm2 are as follows:
>> pm2 stop server.js>> pm2 restart server.js
You can look for more commands on the pm2 website.
Let’s see the security groups attached to the Ubuntu EC2 machine in the private subnet:

So all traffic from the public subnet is allowed. One more test I want to do at this point is to see that if I can access the NodeJS application from the EC2 instance which is in the public subnet (bastian host).
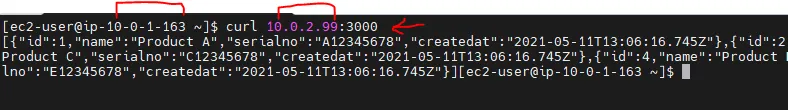
you can see, as expected that we are able to communicate with the Node app (which is running on private EC2 port 3000) from the public EC2 machine.
Next, let’s set up NGINX reverse proxy.
NGINX Configuration
I will try to keep details simple and basic. You can find more info about various configurations online. I also wrote a post on this topic you can look on if needed.
Let’s update the Nginx config file for proxy configuration:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.confThis will open the configuration file in the nano editor. Scroll down until you see a server block, there we need to add location and proxy_pass information for our node application as follows (notice the private IP address of Ubuntu EC2 machine running NodeJS app on port 3000):
location /nodeapp/{ proxy_pass http://10.0.2.99:3000/; }Here is the config file of Nginx on my public EC2 instance.
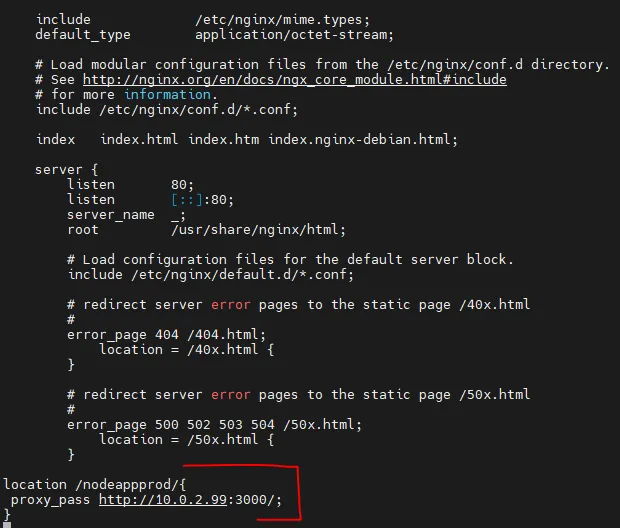
Press Ctrl+X to save and close the file. Restart the NGINX service.
sudo service nginx restart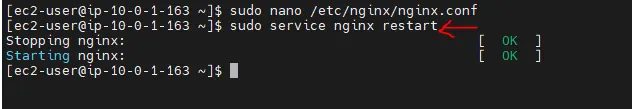
Now, let’s try to access the node application endpoint using browser:
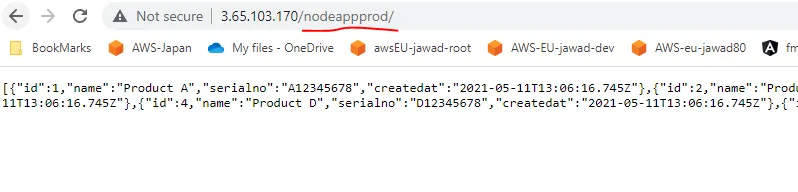
And you can see that we are able to receive the data as expected.
Following is the updated diagram of the current workload:
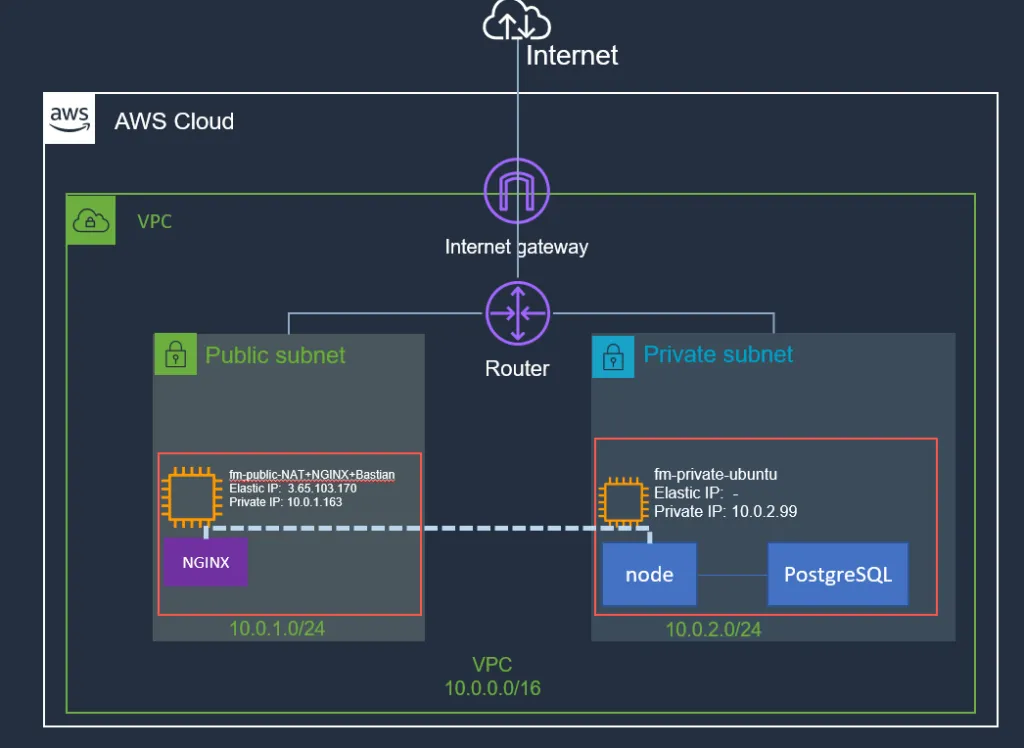
NGNIX is a lightweight and easy-to-use web server. If you like, you can actually introduce multiple location blocks and proxy calls to different services running on different EC2 instances.
Summary
In this post, we set up NGINX on the EC2 instance in the public subnet. We then make a reverse proxy configuration to pass a request to the NodeJS application from the previous post and because that application can connect to the PostgreSQL database, we're able to access the data over HTTP.
This is a very basic, common setup with a web server, application, and database and in the next posts, we will be adding more applications, configurations and enhance this design as needed. Let me know if you have any questions or comments.
Till next time, Happy Coding!

