Design a Fluent API in Java
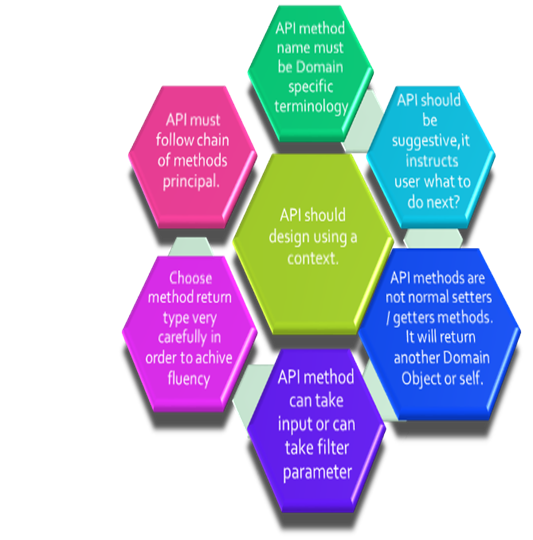
In this article, we will discuss how to design a fluent API in Java. The term Fluent interface was coined by Martin Fowler and Eric Evans. Fluent API means to build an API in such way so that it meets the following criteria:
- The API user can understand the API very easily.
- The API can perform a series of actions in order to finish a task. In Java, we can do it with a series of method calls (chaining of methods).
- Each method's name should be domain-specific terminology.
- The API should be suggestive enough to guide API users on what to do next and what possible operations users can take at a particular moment.
Suppose you want to design an API for a domain, say Retail, so there should be some common terminology that exists in the Retail domain, and for a certain context (Task), it will take a series of actions to finish this task. Say for an invoice generation, it has to follow certain steps.
Now, when you design an API, you should design it such a way that when API users call Billing Service for invoice generation, the users can fluently perform each step in order to complete said generation, and the API will assist users to perform those steps upon invoking Billing Service.
When an API method is invoked by a user, the method will perform its task and returns a Domain Object, which will assist in what to do next — until all steps are executed. Unlike a standard API, it is the API user's job to call API methods in a sequential way to successfully performs a task. So the API users have to know about the service steps very well.
Design A Fluent API:
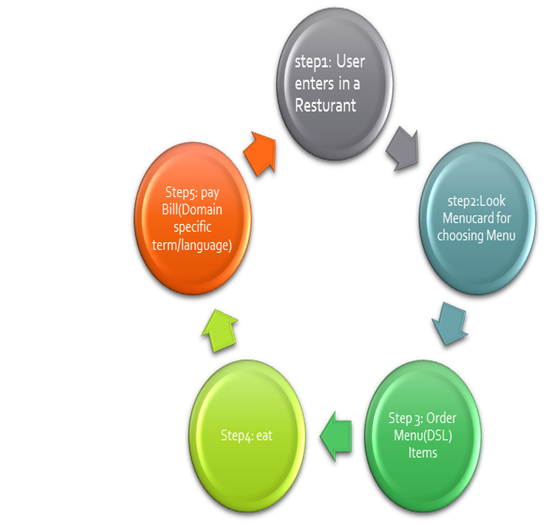
Example: Suppose we want to design an API for a restaurant.
As a customer of this restaurant, one should follow these steps:
In a standard API design, we will do the following:
- Create a "Restaurant" interface.
- Create an implementation class of Restaurant. Compose the Menucard class into it.
- Create getters and setters for restaurant properties like name, address, etc.
- In MenuCard, maintain a list of Items. Expose some methods, like showmenu(), Ordermenu(), etc.
- Each Item has name and cost properties and corresponding getters/setters.
- When the API user calls this API he/she will call a sequence of methods(Enter Restaurant, call showMenu(), then Ordermenu(), etc.) to perform the above steps shown in the picture.
So it is not fluent. A lot of sequential statements need to be performed to complete the task, and the API user has to know the sequence.
Now I will show you how we will design a fluent API.
1. Create an interface IResturant which has two methods
a. Print name of the resturant,notice the return type it returns itself , because after displaying name user wants to see menu card.
b. show() method returns menucard .
Thing to notice : Resturent Implementation is suggestive as it has two methods one is name and another show (next operation user wants to perform)
2. IMenu Implementation has 4 important methods showmenu(),order(),eat(),pay() -all methods return MenuHandler implementation so we can perform one of these action. Again this is Suggestive.
Code Implementation :
Java
package com.example.fluentapi.contract;
public interface IResturant {
public IResturant name(String name);
public IMenu show();
}
package com.example.fluentapi.contract;
public interface IMenu{
public IMenu order(int index);
public IMenu eat();
public IMenu pay();
public IItem get(int index);
}
package com.example.fluentapi.contract;
public interface IItem {
public IItem name();
public Integer cost();
}Implementation
package com.example.fluentapi.impl;
import com.example.fluentapi.contract.IMenu;
import com.example.fluentapi.contract.IResturant;
public class Arsalan implements IResturant{
String name;
String IMenu;
public IResturant name(String name) {
this.name=name;
System.out.println("Enter to hotel :: " + name);
return this;
}
public IMenu show() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArsalanMenuHandler handler = new ArsalanMenuHandler();
handler.showMenu();
return handler;
}
}
package com.example.fluentapi.impl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.fluentapi.contract.IItem;
import com.example.fluentapi.contract.IMenu;
public class ArsalanMenuHandler implements IMenu{
List<IItem> menuList = new ArrayList<IItem>();
List<IItem> selectedList = new ArrayList<IItem>();
public ArsalanMenuHandler()
{
IItem biriyani = new IItem(){
public IItem name()
{
System.out.println("Mutton Biriyani");
return this;
}
public Integer cost()
{
return 180;
}
};
IItem muttonChap = new IItem(){
public IItem name()
{
System.out.println("Mutton Chap");
return this;
}
public Integer cost()
{
return 160;
}
};
IItem firni = new IItem(){
public IItem name()
{
System.out.println("Firni");
return this;
}
public Integer cost()
{
return 100;
}
};
menuList.add(biriyani);
menuList.add(muttonChap);
menuList.add(firni);
}
public IMenu order(int index) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
IItem item (index);
selectedList.add(item);
System.out.println("Order given ::");
item.name();
return this;
}
public IMenu eat() {
for(IItem item : selectedList)
{
System.out.println("eating ");
item.name();
}
return this;
}
public IMenu pay() {
int cost=0;
for(IItem item : selectedList)
{
cost = cost + item.cost();
}
System.out.println("Paying Rupees" + cost);
return this;
}
@Override
public IItem get(int index) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(index <3)
{
return menuList.get(index);
}
return null;
}
public void showMenu(){
System.out.println("MENU IN ARSALAN");
for(IItem item : menuList)
{
item.name();
}
}
}Test Fluent API
package com.example.fluentapi.impl;
public class FluentApiTest {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
new Arsalan().name("ARSALAN").show().order(0).order(1).eat().pay();
}
}Output:
Enter to hotel :: ARSALAN
MENU IN ARSALAN
Mutton Biriyani
Mutton Chap
Firni
Order given ::
Mutton Biriyani
Order given ::
Mutton Chap
eating
Mutton Biriyani
eating
Mutton Chap
Paying Ruppes340
Look How we perform the steps fluently by calling a series of methods.
new Arsalan().name("ARSALAN").show().order(0).order(1).eat().pay();
This is a test example. To make it more polished we need to work on the following:
- The Order method should take MenuItem instead of position, and it also needs to handle Exception scenarios if a MenuItem not found.
- Order should be able to be cancelled.
- Pay must have payment mode. (credit card, debit card, cash)
- Optional tips should be incorporated.
- While eating, the user should be able to order more items, so make an Order functional during that time.
- Tax calculation should be added.

