How to Move IBM App Connect Enterprise to Containers
This article is part of a series. For the previous article, see how we use ODBC as an example to show how to connect to databases from IBM App Connect Enterprise Containers.
This article explains how to install the latest version of the IBM App Connect Operator on an Amazon EKS cluster, and deploy an integration using it. It is part of a broader series on moving to IBM App Connect on containers.
Most of our scenarios in the series so far have assumed that your Kubernetes environment is Red Hat OpenShift. This reduced the steps in our examples significantly as OpenShift pre-integrates a huge number of commonly used capabilities (200+) and performs a number of common steps automatically. However, we recognize that not all enterprises have OpenShift available to them, and for that reason, IBM App Connect is designed and supported to run on any major Kubernetes distribution.
In this example, we’re going to see what additional steps would be required to perform a deployment on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) using the IBM App Connect Operator. In order to keep this post to a reasonable length, we have assumed that the reader has some familiarity with Amazon EKS already, and hence the reason they have taken an interest in this article. As such, we will refer the reader to EKS documentation where necessary rather than repeat it here.
We will set up the EKS environment with the necessary capabilities that would have already been present in OpenShift, then we’ll perform an actual deployment of an integration.
To prepare the environment, we will need to do the following extra steps on Amazon EKS compared to OpenShift:
- Install a certificate manager
- Install the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM)
- Create the Apache CouchDB operator catalogue
- Install the App Connect Operator manually
- Create an Operator Group for the IBM App Connect Operator
- Create the IBM App Connect operator catalogue
- Create the IBM App Connect operator subscription
- Optional: Create App Connect Dashboard
- Create an NGINX Ingress
We only need to do the above preparation once. However, for each integration that needs to be exposed on the network outside the Kubernetes cluster we will need to:
- Create an ingress definition for the integration
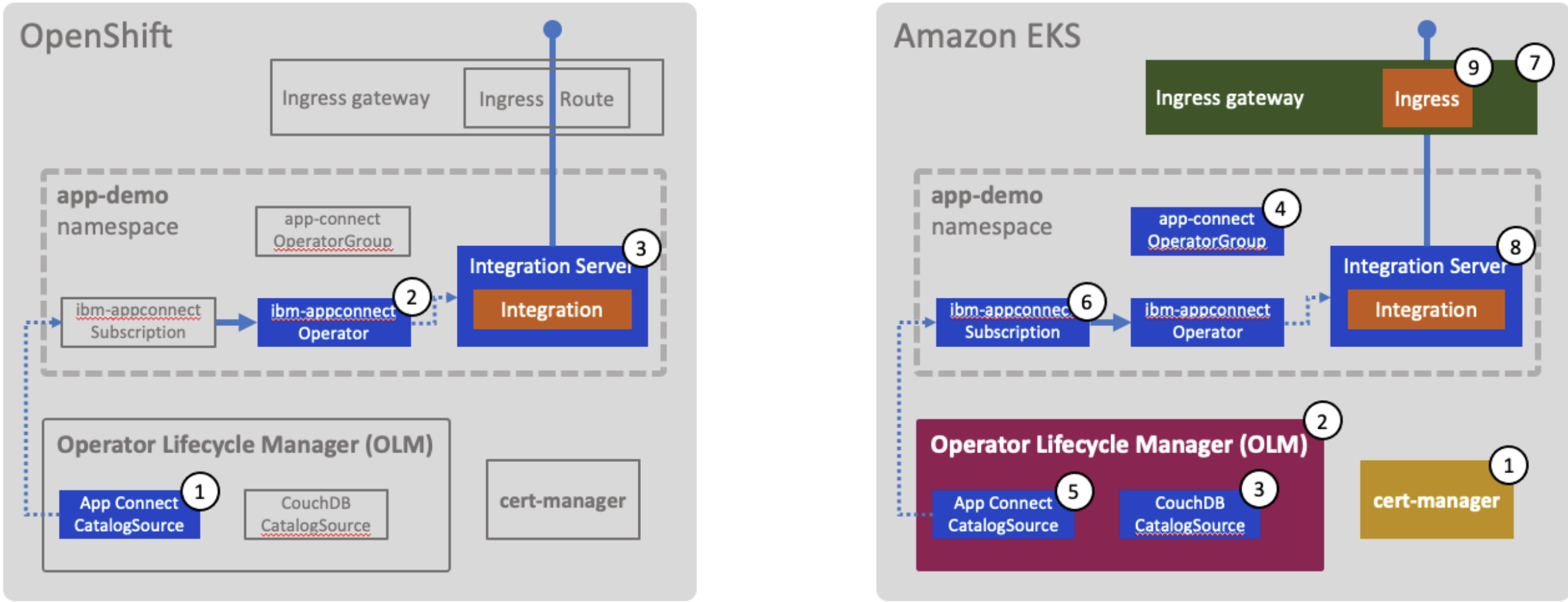
The following diagram provides a visual representation.
In order to follow these instructions, you will need to have the following tools already installed on your local workstation.
- AWS CLI (aws)
- Kubernetes CLI (kubectl)
Everything we will describe in this article is also present (in greater detail) in the IBM App Connect documentation here.
Configure Your AWS and EKS Command Line
Throughout this article, we will be remotely connecting to Amazon EKS from our local command line. We will set up a local configuration such that we don’t need to enter details such as credentials on each aws or kubctl command.
Configure Your AWS CLI
First, we need to configure basic settings (credentials, region, and so on) that the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) uses to interact with AWS.
$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [****************J74P]: AWS Secret Access Key [****************D12u]: Default region name [us-east-1]: Default output format [json]:
There is more information on configuration in the AWS CLI documentation.
Create/Update Your EKS Cluster Configuration
Next we need to create a kubeconfig file that stores credentials for our Kubernetes cluster on EKS.
$ aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <cluster-name>
There is information on creating a kubeconfig in the Amazon EKS documentation.
Install Cert-Manager in Your EKS Cluster
Any communication to components that needs to be secured using TLS (such as HTTPS) will require certificates.
The operator installation requires that you install the Kubernetes certificate management controller (cert-manager) in your cluster to generate and manage the TLS certificates that are required for internal communication, and exposure of web user interfaces. This will also be required later by the integrations we deploy if they expose for example HTTPS APIs.
Cert-manager is a Kubernetes add-on to automate the management and issuance of TLS certificates from various issuing sources. Cert-manager is included in OpenShift, but in EKS it has to be explicitly installed.
These instructions were correct at the time of writing, but feel free to check the documentation for any more recent updates such as the version number of cert-manager.
Install cert-manager using the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.6.1/cert-manager.yaml
You can verify the cert-manager installation using:
$ kubectl get pods --namespace cert-manager
We also need to perform a small patch to cert-manager to ensure any auto-generated secrets that store certificates are automatically removed when there are no longer any owner references. We do this with the following command:
kubectl patch deployment \
cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--type='json' \
-p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args", "value": [
"--v=2",
"--cluster-resource-namespace=$(POD_NAMESPACE)",
"--leader-election-namespace=kube-system",
"--enable-certificate-owner-ref"
]}]'
You can use the following command to confirm patching worked as expected:
kubectl get deployment cert-manager --namespace cert-manager -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.containers[0].args}'
You will get a response like the following showing the values you just added with the previous patch command:
[--v=2 --cluster-resource-namespace=$(POD_NAMESPACE) --leader-election-namespace=kube-system]
Install the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) in Your EKS Cluster
The Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) is a fundamental part of the Operator Framework. It is a Kubernetes application that looks after your operators (such as the IBM App Connect Operator). It makes operators discoverable, ensures that installed operators are kept up to date, manages their dependencies and underpins many of the core aspects of the operators’ functionality. It is installed in OpenShift by default, but this is typically not so in most other Kubernetes distributions, such as EKS.
Install the Operator SDK
The Operator SDK is primarily for building your own operators, but it also happens to include the command needed to install the OLM capability on your Kubernetes cluster. Follow the instructions to install it here:
https://sdk.operatorframework.io
Install the OLM
Use the SDK to install the OLM:
$ operator-sdk olm install
This command completes with a list of the resources that it has created to verify the installation.
You can also verify the OLM installation with:
$ kubectl get crds
The output you should expect to see is documented here along with full details on this step.
Add Apache CouchDB to the Operator Catalog
The IBM App Connect operator has a broader use than just deploying IBM App Connect Enterprise runtimes. It also provides the capabilities for creation of integrations using the App Connect Designer tooling. Due to this known dependency, CouchDB will need to be available in the catalog for the IBM App Connect Operator installation to succeed.
The OLM installed in the last step holds a catalog of available operators. In our OpenShift-based scenarios, CouchDB was available because we had populated the OLM with the whole IBM Catalog, since this is easy to do on OpenShift. In this EKS-based example, we’ve chosen to take a more minimalist approach and we will just populate the catalog with the Operators that we need.
To add a new entry in that catalog, you supply a CatalogSource object. For our CouchDB operator, the catalog source is:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: CatalogSource metadata: name: couchdb-operator-catalog namespace: olm spec: displayName: "IBM CouchDB Operator Catalog" publisher: IBM sourceType: grpc image: icr.io/cpopen/couchdb-operator-catalog:latest updateStrategy: registryPoll: interval: 45m
Place the above into a file named couchdb-catalog-source.yaml
Now run the following command to add it to the OLM catalog.
$ kubectl apply -f couchdb-catalog-source.yaml -n olm
You can verify the operator is available in the catalog with:
$ kubectl get CatalogSources couchdb-operator-catalog -n olm
Install the IBM App Connect Operator
Installation of the App Connect Operator itself involves three steps:
- Create an OperatorGroup.
- Add App Connect to the operator catalog.
- Install the operator by creating a Subscription.
In our previous examples, OpenShift’s OperatorHub made reasonable assumptions and turned this into a single, relatively straightforward step via the web console. In EKS, we have to do each step manually.
Create an OperatorGroup for the IBM App Connect Operator
The OLM runs with high levels of privilege within Kubernetes, and can grant permissions to operators that it deploys. An OperatorGroup provides a mechanism for controlling what permissions are granted by OLM, and in which namespaces. If Kubernetes administrators have any security concerns relating to OLM, this is a critically important area to explore.
A single OperatorGroup must be created in each namespace that will contain operators. The namespace for our operator will be ace-demo and we need to create an OperatorGroup within that.
Create the app-connect namespace for our operator:
$ kubectl create namespace ace-demo
Create an OperatorGroup definition by creating a file named appconn-operator-group.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: OperatorGroup metadata: name: app-connect-operator-group namespace: ace-demo spec: targetNamespaces: -ace-demo
It is of course important that the namespace above matches with the namespace into which we later try to deploy our integration into. We have chosen the same namespace as we have been using for our earlier scenarios.
In a production installation, you might choose to have the operator namespace different to the target namespace, and create a separate ServiceAccount to reduce the permissions made available to the IntegrationServer. However, a single namespace is sufficient for our simple example.
Now create the OperatorGroup.
$ kubectl apply -f appconn-operator-group.yaml
Add IBM App Connect to the Operator Catalog
OLM doesn’t yet know the IBM App Connect operator exists, or where to get it from. We need to create the entry in the OLM catalog by creating a CatalogSource object.
Create a file named appconn-catalog-source.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: CatalogSource metadata: name: ibm-appconnect-catalog namespace: olm spec: displayName: "IBM App Connect Operator Catalog k8S" publisher: IBM sourceType: grpc image: icr.io/cpopen/appconnect-operator-catalog-k8s updateStrategy: registryPoll: interval: 45m
Note that the namespace for the CatalogSource is always olm.
Now add it to the OLM catalog:
$ kubectl apply -f appconn-catalog-source.yaml -n olm
You can verify the catalog entry using:
$ kubectl get CatalogSources ibm-appconnect-catalog -n olm
Install the Operator Using a Subscription
For this final step, you might have been expecting some simple command to install an operator. However, as I’m sure you’ve gathered by now, Kubernetes works declaratively, and doesn’t like being told what to do! It likes you to "declare" what you want, then it works out how, and indeed when to do it.
Installing an operator on the OLM follows this same pattern. You declare to the OLM that you would like it to "subscribe" to a particular operator in the catalog. It then takes on the task of downloading the current version of it and instantiating it. There are many advantages to this declarative approach. For example, we can declare that we want to follow a particular "channel" of updates to the operator; for example, we might want every update, or just stable releases and so on. We can also declare whether or not it should update the operator automatically or not.
To create a subscription to the IBM App Connect Operator, create a file named appconn-sub.yaml with the following contents:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: ibm-appconnect namespace: ace-demo spec: channel: v3.1 name: ibm-appconnect source: ibm-appconnect-catalog sourceNamespace: olm
Once again, pay close attention to the namespaces. The metadata.namespace must be the one we will be deploying our integration to. The spec.sourceNamespace is always olm.
You will notice that we will be subscribed to the “v3.1” channel. This means we’re subscribing to a specific version of the operator which was correct at the time of writing. Do check the current documentation to see if a different version is now recommended.
Add the subscription:
$ kubectl apply -f appconn-sub.yaml
To verify that the operator has installed:
$ kubectl get csv

The important field is the PHASE, which should have a status of Succeeded. Note that you may need to specify a namespace, or perhaps use the –all-namespaces option.
Creating an Ingress for Your EKS Cluster
This step is arguably optional since the operator’s installation isn’t actually dependent on it. However, at this point, your cluster is unable to receive requests from the outside world.
It would be rare to find an integration that didn’t need to receive some form of request from beyond the EKS cluster. As a case in point, our example in the next post will expose itself via HTTP. To permit HTTP requests from beyond the cluster, we will therefore require what is known in Kubernetes as an "ingress gateway" in order to make the integration callable over the public internet. Again, this is something that is implemented in OpenShift cluster by default, but in EKS you need to create this explicitly.
Use the following command to create a basic ingress gateway based on the NGINX runtime. There are many other ways to create an Ingress depending on your requirements.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-0.32.0/deploy/static/provider/aws/deploy.yaml
It is beyond the scope of this post to explore the deployment file for this ingress gateway, but there is a good blog post discussing it here.
Optional: Create an Instance of the App Connect Dashboard
As we’ve previously shown in Scenario 2a, you can deploy and administer App Connect Integration Servers completely from the command line, and that is all we need for this example. However, there is a user interface available, known as the App Connect Dashboard. If you want to use this user interface, you should at this point explicitly create an instance of the dashboard. The instructions for this would be the same as those in Scenario 2b, but with one addition. You must create an Ingress such that the dashboard UI is available beyond the EKS cluster as documented here.
Deploy Your Integration
So, that’s all the one-time preparation done and we can move on to deploying an actual integration.
We can now deploy in exactly the same way as we did in our previous scenarios. However, note, there will be one additional step that we didn’t have to do in Scenario 2a; the creation of an Ingress definition.
We’ll provide the absolute minimum instructions here, but feel free to go back to the Scenario 2a article if you want a refresh on the concepts and the reasoning behind each step. The main difference is that instead of working with OpenShift, using the oc command, we’ll instead be using the essentially identical Kubernetes command kubectl.
1. Create the Barauth Configuration Object
Create a text file named github-barauth.yaml with the below contents.
apiVersion: appconnect.ibm.com/v1beta1
kind: Configuration
metadata:
name: github-barauth
namespace: ace-demo
spec:
data: eyJhdXRoVHlwZSI6IkJBU0lDX0FVVEgiLCJjcmVkZW50aWFscyI6eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6IiIsInBhc3N3b3JkIjoiIn19Cgo=
description: authentication for github
type: barauthYou may remember from Scenario 2a that the data section is the base64 encoded string for an 'empty' password since we are pulling the BAR file from public github.
Apply the barauth configuration definition to Kubernetes.
$ kubectlapply -f github-barauth.yaml
2. Create an Integration Server for the Simple Integration
Deploy an IBM App Connect certified container with a link to our simple BAR by creating a file named http-echo-service.yamlwith the following contents.
apiVersion: appconnect.ibm.com/v1beta1
kind: IntegrationServer
metadata:
name: http-echo-service
labels: {}
spec:
adminServerSecure: false
barURL: >-
https://github.com/amarIBM/hello-world/raw/master/HttpEchoApp.bar
configurations:
- github-barauth
createDashboardUsers: true
designerFlowsOperationMode: disabled
enableMetrics: true
license:
accept: true
license: L-KSBM-C37J2R
use: AppConnectEnterpriseProduction
pod:
containers:
runtime:
resources:
limits:
cpu: 300m
memory: 350Mi
requests:
cpu: 300m
memory: 300Mi
replicas: 1
router:
timeout: 120s
service:
endpointType: http
version: '12.0'
Note that strictly speaking you could set createDashboardUsers to false if you know you are not creating an instance of the dashboard.
Create Integration Server with the following command:
$ kubectlapply -f http-echo-service.yaml
You should receive the confirmation:
integrationserver.appconnect.ibm.com/http-echo-service created
3. Create Ingress Object
This is the final extra step that you have to do on EKS compared to OpenShift. Our simple integration receives requests over HTTP and these may come from the public internet. To enable a container to receive requests from outside of the EKS cluster, you will need to create a definition on the ingress gateway we created earlier.
Create a definition file named is-ingress.yaml with the following contents, taking care to replace <external-hostname> with the correct value based on the instructions that follow:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: http-echo-service-ingress
namespace: ace-demo
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
rules:
- host: <external-hostname>
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: http-echo-service-is
port:
number: 7800
Here are some brief explanations for some of the relevant fields in the ingress definition file:
- metadata.name – This can be any name, but you should use a naming convention that helps to identify the relationships with the Integration Server, i.e.
<deployment-name>-ingress. - metadata.namespace – The namespace in which you deployed the Integration Server.
- spec.rules[].http.paths[].backend.service.name – This value must match the service created when the Integration Server was deployed. The name is going to be the name of the Integration Server instance followed by '-is', something like <deployment-name>-is. You can use command
kubectl get services -n $NAMESPACEto confirm the name.
The subtlety here is that you must work out a suitable value for <external-hostname>in the spec.rules[].host field. This will ultimately be the external address external consumers will use to call the integration. What you use for this value depends on your DNS setup. The most important thing is that it has a prefix that allows the ingress gateway to uniquely route traffic to your integration serverpod. A simple example might be something like:
<IntegrationServerDeploymentName>.yourdomain.com
which in our case would be:
http-echo-service.yourdomain.com
However, it’s worth considering whether this is unique enough. Remember, the ingress gateway we created earlier is cluster-wide, so what if you had another deployment of the same integration in another namespace?
If you look back at Scenario 2a you’ll see that, this ingress definition was created for us automatically by the ACE Operator. The operator only currently does this when running in OpenShift, because it knows there is always an Ingress gateway present. (Note that ingress definitions in OpenShift are called Routes).
The prefix that the Operator created automatically in Scenario 2a was constructed from three things.
1. The integration server deployment name http-echo-service
2. The protocol http (we could be exposing the same service over HTTP or HTTPS)
3. The namespace ace-demo
So the prefix ended up being http-echo-service-http-ace-demo. A little complicated perhaps, but with a reasonable guarantee of uniqueness across the cluster.
So, a more unique value for the full <external-hostname> might be something like:
http-echo-service-http-ace-demo.yourdomain.com
Do You Have a DNS Configured?
If you have an already established EKS environment in your organisation, it is likely that you also have a DNS configured. However, if you are using a temporary test environment, it is possible that you do not. In this case you may need to use a wildcard DNS service such nip.io. These allow you to use any prefix and force a mapping to an IP address that is embedded in the hostname. So, for example:
http-echo-service-http-ace-demo.23.72.153.69.nip.io
will simply be routed to the 23.72.153.69 IP address.
In order to get the values needed to configure this field if using nip.io you need to get the IP Address associated to the EKS cluster load balancer. You can use this command:
Kubectl get services -n ingress-nginx -o wide
This will result in something like the following output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.88.168 abc123.elb.amazonaws.com ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.100.143.60 <none>
- From the output grab the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) associated with the
ingress-nginx-controller. This is the address which can be called from outside the cluster over the public internet. - Run the
nslookupcommand on the FQDN to get the IP address. For example, based on the preceding output, we would use the following command.nslookup abc123.elb.amazonaws.comThe output might look something like this:
Server: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx::1111 Non-authoritative answer: Name: abc123.elb.amazonaws.com Address: yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
- From the output get the IP Address
(yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy), and build up the nip.io URL like this:http-echo-service-http-ace-demo.yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.nip.ioThis then is the value that you should use for
<external-hostname>in the ingress definition file above. - Deploy the ingress object using the following command
kubectl apply -f is-ingress.yamlOnce the ingress configuration has been deployed your micro-integration is ready to receive traffic from outside the EKS cluster.
- Test the integration
Verify the status of Integration Server pod and ensure that its status has changed to
1/1 Running.For example:$ kubectl get podsNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE http-echo-service-is-64bc7f5887-g6dcd 1/1 Running 0 67s
Invoke the service using curl command using the first URL you configured in the ingress definition. So if you have DNS set up:
$ curl -X POST http://http-echo-service-http-ace-demo. yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.yourdomain.com/Echoor if you don’t have DNS configured, then use the nip.io url we constructed earlier - replacing with the IP address you found for the:
$ curl -X POST http://http-echo-service-http-ace-demo. yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.nip.io/EchoYou should receive a response similar to the following, letting you know that your request made it into the container and returned back.
<echo><datestamp>2021-10-30T06:03:59.717574Z</datestamp></echo>
Conclusion
So that’s it, you’ve done it! You’ve deployed a (very) simple flow from an IBM Integration Bus environment into an IBM App Connect container on Amazon EKS. There are a few more steps compared to OpenShift, but most of those are up front to prepare the environment and are then in place for all subsequent deployments. There are one or two other differences worth noting when installing on a non-OpenShift based environment, and these are documented here.
The following diagram provides a summary of the activities and components we have deployed in the EKS cluster.

The steps would be largely the same for any non-OpenShift Kubernetes environment such as the Azure Red Hat OpenShift service, or indeed a self-managed non-OpenShift Kubernetes cluster.
Acknowledgement and thanks to Kim Clark for providing valuable input to this article.

